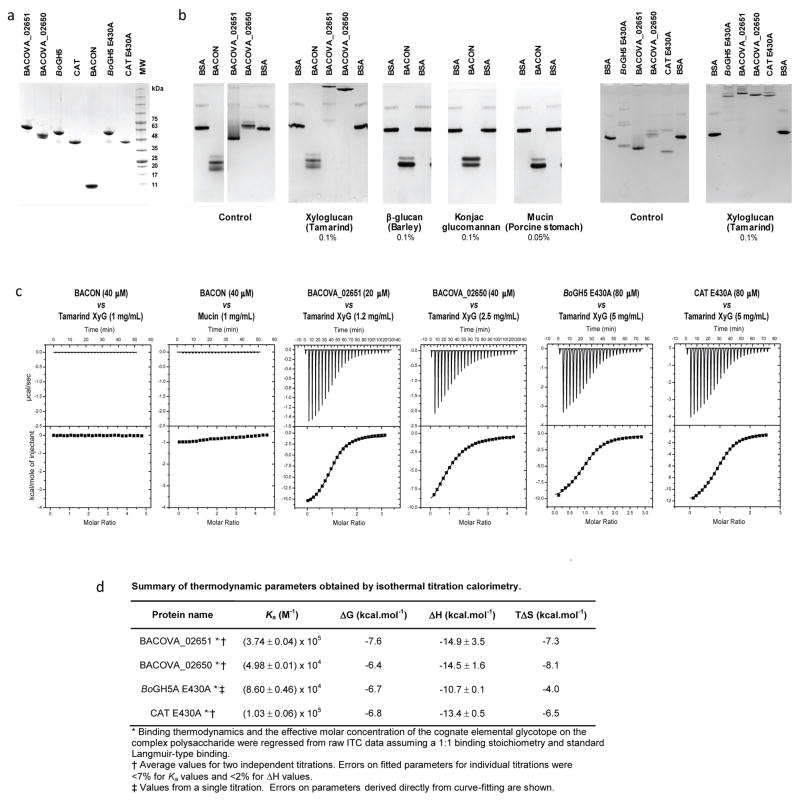
Figure ED4.
Non-catalytic interaction of BoGH5A variants, SusD-like Bacova_02651 and Bacova_02650 of the XyGUL with polysaccharides. a. SDS-PAGE of recombinant proteins (representative data from at least three preparations for each protein is shown). b. Affinity gel electrophoresis (representative data from at least two gels for each experimental condition). c. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC); the upper graph in each pair shows the raw heat during titration, while the lower graph shows the integrated heats after correction. d. Association constants and thermodynamic parameters obtained from ITC data. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was used as non-interacting negative control protein. Other protein names were abbreviated as follows: BACON, residues Cys1-Tyr97 corresponding to the BACON domain of BoGH5A; Bacova_02651, SusD-like XyGUL gene product; Bacova_02650, SusE-positioned XyGUL gene product; BoGH5A E430A, full-length (Cys1 to Asn470) catalytic nucleophile mutant of BoGH5A; CAT E430A, catalytic nucleophile mutant of the BoGH5A catalytic domain only (Ser98 to Asn470). Reducing-sugar assays confirmed the catalytic mutants had no detectable hydrolytic activity on xyloglucan (data not shown), while an active variant (i.e., E430) of CAT had a 2-fold higher specific activity than the full-length, wild-type BoGH5A at saturating xyloglucan concentrations (0.5 – 3 mM).