Table III.
Definitions and values of model parameters used in the model of multiple myeloma-induced bone disease.
| Parameters | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
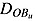 |
Differentiation rate of osteoblast progenitors | 3.24e + 2/day (estimated) |
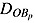 |
Differentiation rate of osteoblast precursors | 3.67e-1/day (estimated) |
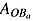 |
Rate of elimination of active osteoblasts | 3.00e-1/day 14 |
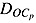 |
Differentiation rate of osteoclast precursors | 1.73e-1/day (estimated) |
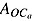 |
Rate of elimination of active osteoclasts | 1.20/day 14 |
| KD1,TGFβ | Activation coefficient related to growth factors binding on OBu | 4.28e-4 pM (calculation by GA) |
| KD2,TGFβ | Repression coefficient related to growth factors binding on OBp | 2.19e-4 pM (estimated) |
| KD3,TGFβ | Activation coefficient related to growth factors binding on OCa | 4.28e-4 pM 14 |
| KD1,PTH | Activation coefficient for RANKL production related to PTH binding | 2.09e + 1 pM (calculation by GA) |
| KD2,PTH | Repression coefficient for OPG production related to PTH binding | 2.21e-1 pM 14 |
| KD,TGFβ,IL6,act | Half-maximal concentration of TGF-β on promoting the production of IL-6 | 1.2e-4 pM (calculation by GA) |
| KD,IL6,RANKL,act | Half-maximal concentration of IL-6 on promoting the production of RANKL | 0.2 pM (calculation by GA) |
| KD,RANKL | Activation coefficient related to RANKL binding to RANK | 4.12e + 1 pM (estimated) |
| α | TGF-β content stored in bone matrix | 1.00 pM/% 14 |
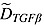 |
Rate of degradation of TGF - β | 2.00e + 2/day 42 |
| βPTH | Rate of synthesis of systemic PTH | 9.74e + 2 pM/day 43 |
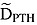 |
Rate of degradation of PTH | 3.84e + 2/day 43 |
| βIL6 | Rate of synthesis of IL - 6 per cell | 1.20e + 7/day27,44 |
| DIL6 | The degradation rate of IL-6 | 4.99e + 1/day 45 |
| IL6max | The maximum concentration of IL-6 | 8.04e-1 pM 46 |
| βOPG | Minimum rate of production of OPG per active osteoblast | 5.02e + 6/day (estimated) |
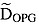 |
Rate of degradation of OPG | 4.16/day 25 |
| OPGmax | Maximum possible OPG concentration | 7.98e + 2 pM 65 |
| βRANKL | Production rate of RANKL per cell | 8.25e + 5/day (estimated) |
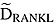 |
Rate of degradation of RANKL | 4.16/day 47 |
| RRANKL | Maximum number of RANKL on the surface of each osteoblastic precursor | 3.00e + 6 14 |
| RANK | Fixed concentration of RANK | 1.28e + 1 pM 14 |
| KA,OPG | Association rate constant for RANKL binding to OPG | 5.68e-2/pM 48 |
| KA,RANK | Association rate constant for RANKL binding to RANK | 7.19e-2/pM 48 |
| Kres | Relative rate of bone resorption (normalised with respect to normal bone resorption) | 2.00e + 2%/(pM day) 49 |
| Kform | Relative rate of bone formation (normalised with respect to normal bone resorption) | 3.32e + 1%/(pM day) (calculation by GA) |
| DMM | MM proliferation controlled by IL-6 and BMSC-MM adhesion | 5.50e-2/day (estimated) |
| AMM | Rate of elimination of active MM cells | 2.00e-3/day 50 |
| MMmax | Maximum possible MM concentration | 1.98 pM 51 |
| KD,VCAM1,MM,act | Half-maximal concentration of VLA - 4 on promoting the MM cells production | 1.5667e-4/pM (calculation by GA) |
| KD,VLA4,IL6,act | Half-maximal concentration of VLA - 4 on promoting the IL-6 production | 1.88e + 4/pM (calculation by GA) |
| KD,IL6,MM,act | Half-maximal concentration of IL - 6 on promoting the MM cells production | 1.2151e-5 pM (calculation by GA) |
| KD,SLRPs,MM,rep | Half-maximal concentration of SLRPs on promoting the MM cells production | 1.306e + 9 pM (calculation by GA) |
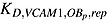 |
Half-maximal concentration of VCAM - 1 on repressing the differentiation of OBp | 1.4e-1 pM (calculation by GA) |
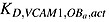 |
Half-maximal concentration of VCAM - 1 on promoting the apoptosis of OBa | 2.2e-1 pM (calculation by GA) |
| βVLA4 | Rate of synthesis of VLA - 4 per cell | 2.04e + 6/day (estimated) |
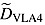 |
Rate of degradation of VLA-4 | 1.5/day (estimated) |
| RVLA4 | Maximum number of VLA-4 expressed on the surface of MM cells | 5.6e + 4 52 |
| VCAM1tot | Total concentration of VCAM-1 | 1.92 pM 52 |
| KA,VCAM1 | The association rate for VLA-4 binding to VCAM-1 | 8.3e-2/pM 53 |
| DOPG,MM | The degradation rate of OPG by MM cells | 4.16/(pM day) (estimated) |
RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; OPG, osteoprotegerin; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta; PTH, parathyroid hormone; IL-6, interleukin-6; SLRP, small leucine-rich proteoglycan; VLA-4, very late antigen-4; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; MM, multiple myeloma; GA, genetic algorithm.
