Figure 1.
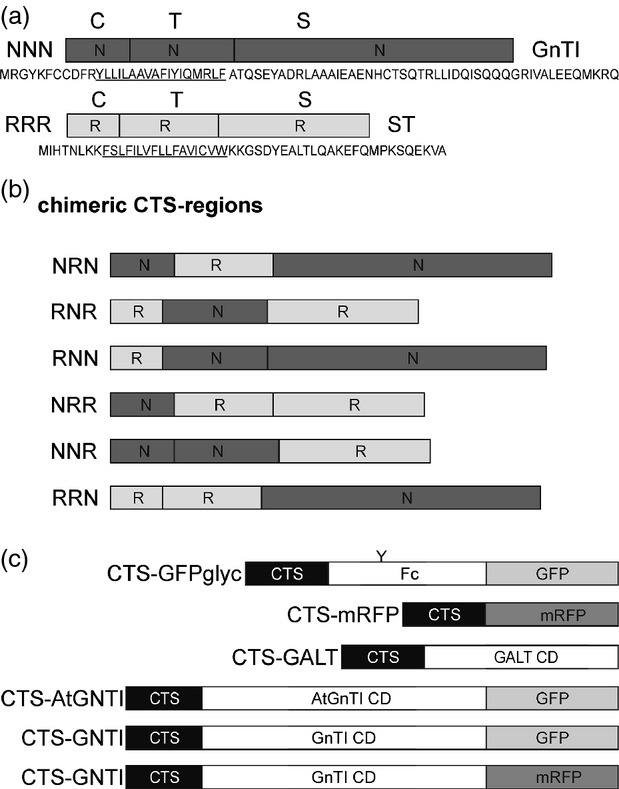
Schematic presentation of protein fusions.(a) The cytoplasmic transmembrane and stem (CTS) regions of N–acetylglucosaminyltransferase I (GnTI, NNN) and α–2,6-sialyltransferase (ST, RRR), and corresponding amino acid sequences, are shown. C denotes the short N–terminal cytoplasmic tail; T indicates the transmembrane domain (underlined in the corresponding amino acid sequence) and S depicts the stem region. Domains marked by ‘N’ are from Nicotiana tabacum GnTI and ‘R’ indicates domains from ST.(b) Schematic presentation of the chimeric CTS regions derived by exchange of C, T or S regions (NRN, RNR, RNN, NRR, NNR, RRN).(c) Schematic presentation of reporter protein domains that were fused to the CTS regions. ‘Y’ denotes the single N–glycosylation site present in GFPglyc. The conserved Fc domain from human IgG1 is used for affinity purification. GALT CD harbors the catalytic domain (CD) of human β–1,4-galactosyltransferase. AtGnTI CD harbors the catalytic domain of Arabidopsis thaliana GnTI. This construct is expressed under the endogenous GnTI promoter from A. thaliana. GnTI CD harbors the catalytic domain of N. tabacum GnTI.
