Figure 1. Malt1 C472A knock-in mice express a catalytically inactive form of Malt1.
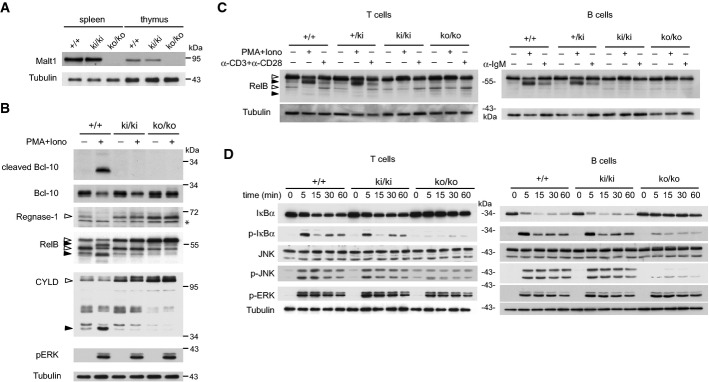
- Immunoblot analysis of spleen and thymus of Malt1-proficient (+/+), Malt1-deficient (ko/ko), or knock-in mice expressing a C472A mutant form of Malt1 (ki/ki).
- Immunoblot analysis of splenocytes, incubated with or without PMA and ionomycin (PMA+Iono) for 30 min, for the presence and cleavage of Malt1 substrates. Cleaved Bcl-10 was detected using an antibody directed against the cleavage-specific neoepitope.
- Immunoblot analysis of purified splenic T or B cells, stimulated with or without PMA and ionomycin (PMA+Iono) for 30 min or the indicated antibodies (anti-IgM, α-IgM; anti-CD3 and anti-CD28, α-CD3+α-CD28) for 60 min, for the presence and cleavage of RelB.
- Immunoblot analysis of purified T cells or B cells of wild-type (+/+), knock-in (ki/ki), and knock-out (ko/ko) mice, stimulated with PMA and ionomycin (PMA+Iono) for the indicated times.
Data information: Samples in (B) and (C) were treated with MG-132 prior to stimulation to prevent proteasomal degradation of the RelB cleavage fragments. Immunoblotting for tubulin served as a loading control. Open and black arrowheads indicate uncleaved and cleaved Malt1 substrates, respectively. Asterisk (*) indicates an unspecific band. Cells of three mice per genotype were pooled in (C) and (D). Data are representative of three (A), four (B, D), and two (C) experiments.
Source data are available online for this figure.
