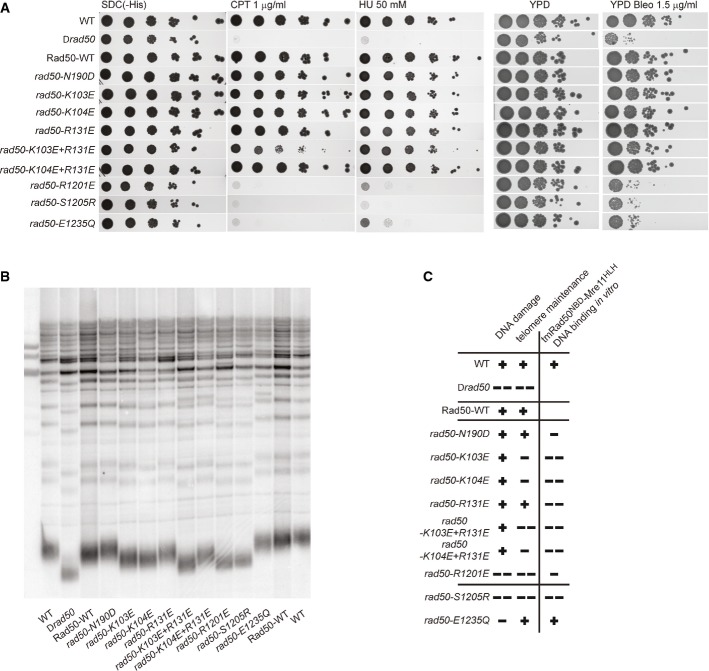
Figure 4. In vivo analysis of Rad50 mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- Effects of rad50 mutants on S. cerevisiae survival in the presence of DNA-damaging agents. Plate survival assays show that R1201ScE, S1205ScR, and E1235ScQ mutants are deficient in the DNA damage response, comparable to the Δrad50 strain. K103ScE + R131ScE double mutant shows partially inhibited DNA damage response.
- Telomere maintenance assays show altered telomere metabolism for mutations or double mutations at the proposed Rad50 DNA-binding groove (K103ScE, K104ScE, K104ScE + R131ScE, R1201ScE) and the signature motif mutant S1205ScR. A notable exception is the Walker B mutant E1235ScQ, which is not proficient in ATP hydrolysis, suggesting that the ATP-bound, engaged Rad50 dimer is essential for the role of MRN at telomeres.
- Summary of S. cerevisiae phenotypic behavior in DNA repair and telomere maintenance compared with the effect of the corresponding tmRad50 mutations on DNA binding in vitro.