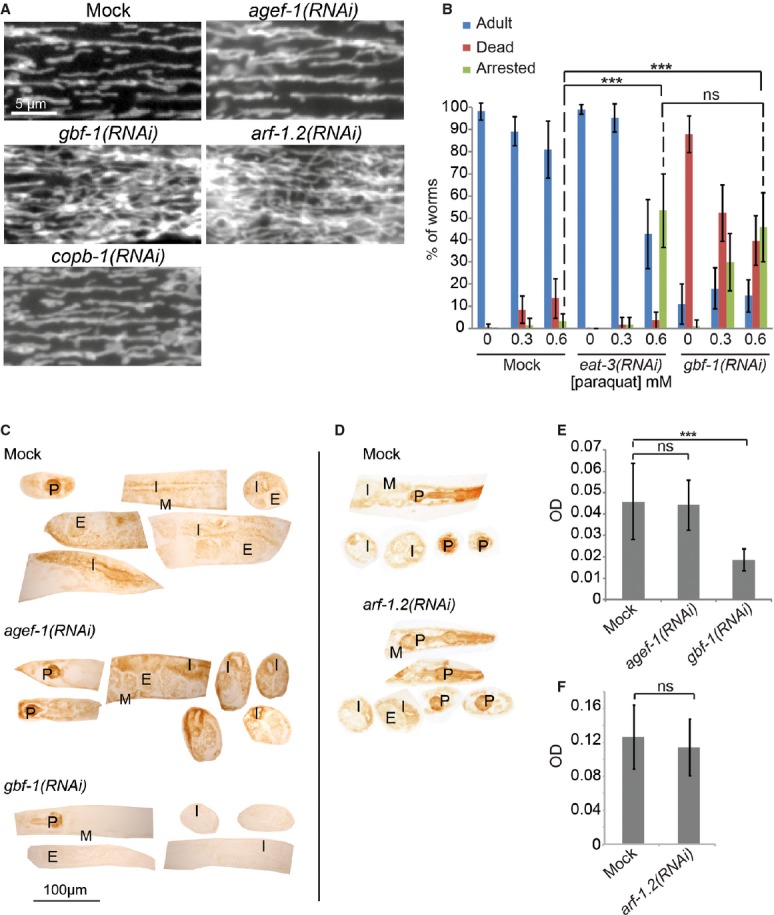
Live imaging of TOM70::GFP in C. elegans muscle cells. In wild-type, agef-1(RNAi) and copb-1(RNAi) muscle cells, mitochondria show the typical tubular morphology along the length of the contractile apparatus, while mitochondria in gbf-1(RNAi) and arf-1.2(RNAi) muscle cells formed a hyper-connected network.
gbf-1(RNAi) worms are ROS sensitive. eat-3(RNAi) served as a positive control. The experiment was performed four times in triplicates of 20 worms each. Standard deviation is given. For significance testing, one-way ANOVA was used, followed by a Tukey's test (arrested phenotype at 0.6 mM paraquat: mock versus eat-3(RNAi) P < 1 × 10−6; mock versus gbf-1(RNAi) P < 1 × 10−6; eat-3(RNAi) versus gbf-1(RNAi) P = 0.79).
The enzymatic activity of cytochrome c oxidase is decreased in somatic tissues and the gonad of gbf-1(RNAi) worms compared to wild-type and agef-1(RNAi). Representative examples are shown.
The enzymatic activity of cytochrome c oxidase was not decreased in arf-1(RNAi) compared to wild-type.
Light microscopic quantification of the resulting optical density (OD) in the body wall muscles. Standard deviation is indicated by error bars. Mock: n = 20, agef-1(RNAi): n = 24, gbf-1(RNAi): n = 25. The statistically significant difference as indicated with asterisks between mock and gbf-1(RNAi) (P < 1 × 10−7) was determined by a t-test (two-tailed, unequal variance).
Analysis as in (E). Mock: n = 13, arf-1(RNAi): n = 12. Mock and arf-1(RNAi) are statistically significantly different (P < 7 × 10−5). P, pharynx; I, intestine; G, gonad; E, embryos; M, muscle.