Figure 5. RNAi-mediated downregulation of Amun in EBs rescues the EE cell bias caused by loss of esg.
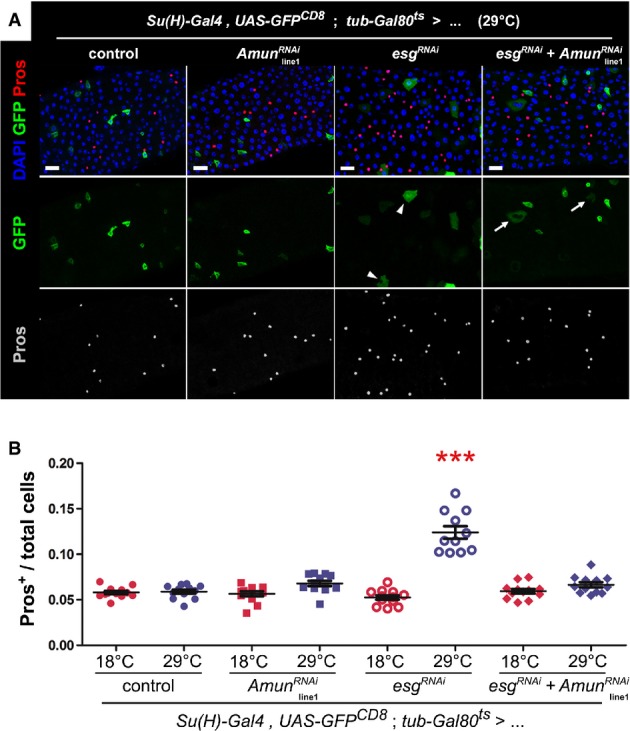
- Immunostaining of midguts following EB-restricted co-downregulation of Amun and esg. Midguts from flies of the indicated genotypes were incubated for 6 days at 29°C and stained for DAPI (all nuclei), GFP (EBs) and Pros (EE cells). “Control” = the Su(H)ts driver stock outcrossed to wild-type flies. The AmunRNAi construct shown is inserted on chromosome II (“line1”; Supplementary Fig S6A and B shows the same experiment with an independent insertion of the same AmunRNAi construct on chromosome X, or “line2”). The esgRNAi flies also carry a UAS-GFPnls construct in the background (to control for GAL4 titration), which explains the nuclear GFP staining of EBs in these midguts. Notice that the alterations in EB morphology caused by Esg knockdown (arrowheads) are only partially rescued by the co-expression of AmunRNAi (arrows; see also Supplementary Fig S6A). Scale bars = 20 μm.
- Abrogation of EE cell enrichment by co-downregulation of Esg and Amun. CellProfiler was used to quantify relative EE cell proportions (as before). Genotype-matched controls were kept for 10–11 days at 18°C. *** denotes the only sample that was significantly different from all other samples in the set, including its genotype match at 18°C (P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA/Bonferroni test).
