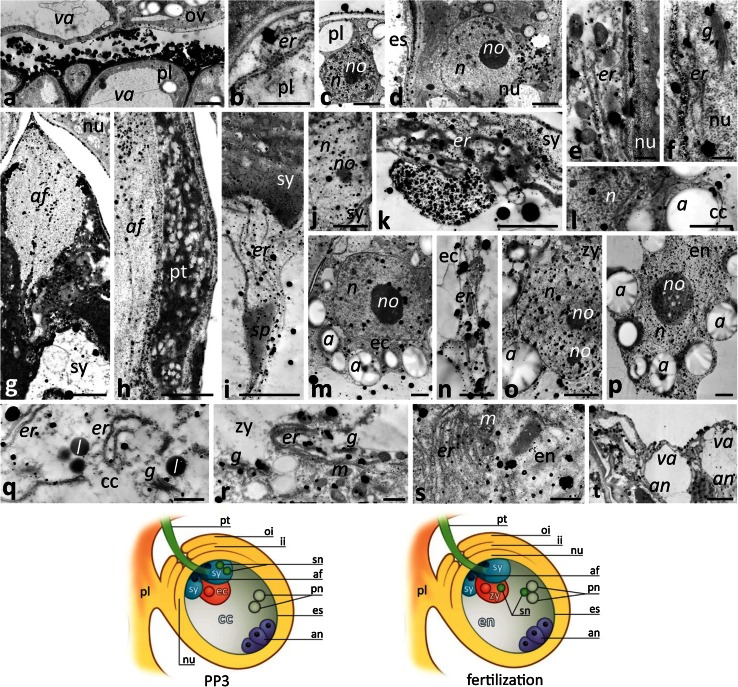
Fig. 5.
Localization of loosely bound Ca2+ by potassium antimonate precipitation in the Petunia placental tissue and at the micropylar end of the ovule during the PP3 stage and at fertilization. a–c Placenta tissue (pl); d–f nucellus (nu); g–k the receptive synergid (sy) penetrated by the pollen tube (pt); l, q the central cell (cc); m, n the egg cell (ec); o, r the diploid zygote (zy); p, s the developing endosperm (en); t degenerating antipodals (an). Cartoons show the ovules at the PP3 stage during sperm cells deposition within the receptive synergid and at fertilization. a amyloplast, af filiform apparatus, er endoplasmic reticulum, es embryo sac, g Golgi stack, ii inter integument, l lipid drop, m mitochondrium, n nucleus, no nucleolus, oi outer integument, ov ovule, pn polar nuclei, sn sperm nucleus, sp sperm cell, va vacuole. Bars 2 μm (a, c, d, g, m, o–p, t), 1 μm (n), 500 nm (b, e, f, q–s)