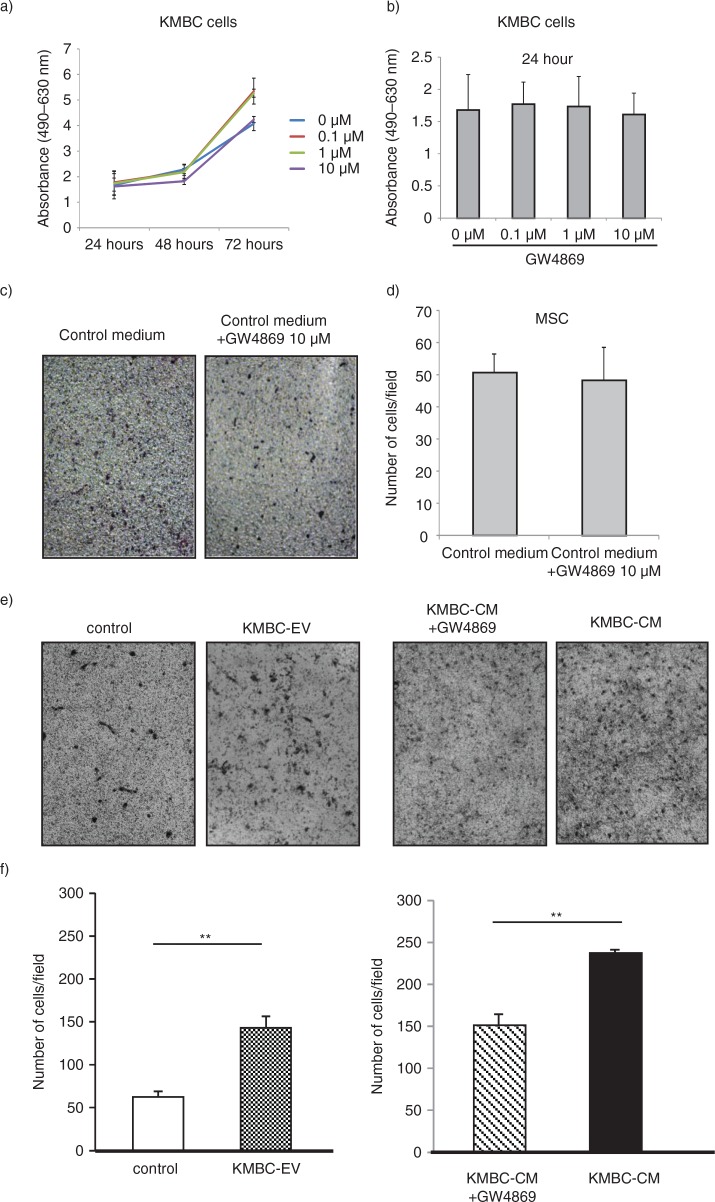
Fig. 4.
KMBC-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) increase migration of MSCs. (a, b) KMBC cells were incubated with varying concentrations of GW4869, an inhibitor of ceramide synthesis that reduces EV release. Cell viability was assessed using an MTS assay. Bars express the mean value±SEM of 3 separate studies. (c–f) Migration of MSCs across a basement membrane was assessed using transwell migration assays. Representative staining of migratory cells and quantitative data representing the mean±SEM of 3 separate studies are shown. (c, d) The effect of control medium with or without GW4869 on migration of MSCs was assessed. GW4869 did not significantly affect migration of MSCs. (e, f) MSCs were cultured alone or in the presence of KMBC cell–derived EVs (KMBC-EVs), conditioned medium (CM) from KMBC cells or CM from KMBC cells incubated with GW4869. KMBC-EVs significantly increased migration of MSCs. Similarly, exposure to CM from KMBC cells also increased migration, but this was reduced in the presence of GW4869.