Fig 1.
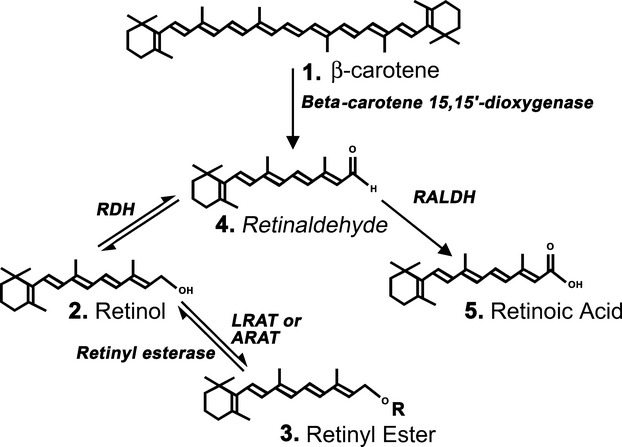
Chemical structures of retinoid family members. β-carotene (structure 1) is cleaved by β-carotene 15,15′-monooxygenase to form two molecules of retinaldehyde (structure 4). The double arrow between retinol (structure 2) and retinaldehyde (structure 4) indicates the interconversion between the two retinoids catalyzed by retinol dehydrogenases (RDHs) primarily RDH1 and RDH10 and dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 9 (DHRS9). The single arrow between retinaldehyde (structure 4) and retinoic acid (structure 5) indicates the irreversible oxidation catalyzed by retinaldhyde dehydrogenase (RALDH) family members. Esterification of retinol is carried out by lecithin:retinol acyltransferase (LRAT) or acyl-CoA:retinol acyltransferase (ARAT). The predominant retinyl ester (structure 3) is retinyl palmitate (r = C15H31).
