Figure 2.
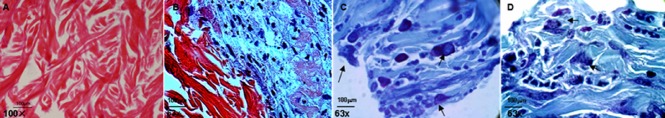
Structure of the FBADM and cell morphology of BMSCs cultured in basal medium or induced in neural differentiation medium on FBADM stained by hematoxylin-eosin or toluidine blue (optical microscopy).
(A) The structure of the FBADM without cells. The woven fibers were predominately collagen, as shown by the hematoxylin-eosin staining of paraffin sections. (B) Cells were cultured in basal medium for 34 days, and the BMSCs proliferated on the surface of the FBADM, assumed a different cell phenotype, and secreted extracellular matrix, predominately collagen, as shown by hematoxylin-eosin staining. The images suggest that BMSCs underwent self-renewal and differentiated along multiple lineages on the FBADM in nurturing long-term in basal medium. (C, D) BMSCs cultured for 3 days in basal medium and then induced for 31 days in neural differentiation medium on the surface of the FBADM. Arrows show visible Nissl bodies in the cell. Scale bars: 100 μm. BMSCs: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; FBADM: fetal bovine acellular dermal matrix.
