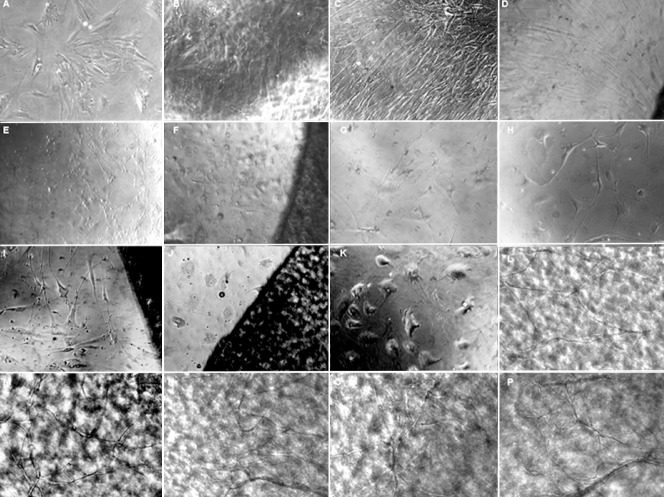
Figure 3.
Proliferation and differentiation of BMSCs in the induced and non-induced conditions with or without FBADM (inverted phase contrast microscopy, × 200).
(A–C) In the negative control without FBADM where the BMSCs were cultured in basal medium for 5, 10, and 25 days, the cells were diamond-shaped and became long fibroblasts-like cells over time. (D) Of the BMSCs cultured with the FBADM in basal medium for 10 days, most of the cells were spindle-shaped and arranged in parallel. Compared to the same culture conditions without the FBADM (B), the cell morphology was somewhat different. (E, F) The cells cultured in basal medium for 3 days and then induced in neural differentiation medium for 2 days. In the positive control (E) without FBADM, and (F) with FBADM, the cell morphology was changed after induction in neural differentiation medium for 2 days compared with (A). (G, H, K) Positive controls of the cells induced in basal medium for 3 days and then in neural differentiation medium for 7 days (compared to B and D), 11 days (compared to I), and 22 days (compared to C, J, L–P). After the same amount of time in culture, the cell morphology was changed in the different conditions, and there were clearly fewer cells in the induced groups than in the non-induced groups. These results indicate that the differentiated BMSCs did not proliferate or proliferated slowly. (I, J) In the cells with FBADM induced in basal medium for 3 days and then neural differentiation medium for 11 days or basal medium for 3 days and then neural differentiation medium for 22 days compared to (H) and (K), the cell morphologies after culture with and without the FBADM were different for the same induction conditions. These differences in BMSC differentiation between groups cultured with and without the FBADM suggest that FBADM has some effects on the induction of neuronal differentiation in BMSCs. (L–P) Compared to conditions without FBADM (K) and the round FBADM (J), the BMSCs induced in basal medium for 3 days and then neural differentiation medium for 22 days on the surface of FBADM showed longer neurites that were connected to each other, forming a network-like structure. However, the bodies of the cells without FBADM were larger and the neurites were shorter (K) then the positive controls (G, H). The neurites of the cells on round FBADM (J) were shorter than in (I), and even disappeared over time. The network-like structure on the FBADM indicated that the FBADM provides a platform for the maturation of the neurons, as well as neurite extension and network formation. In addition, if the cells are not removed, the BMSCs grown on the FBADM will proliferate and spontaneously differentiate in basal medium over long-term culture. BMSCs: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; FBADM: fetal bovine acellular dermal matrix.