Figure 5.
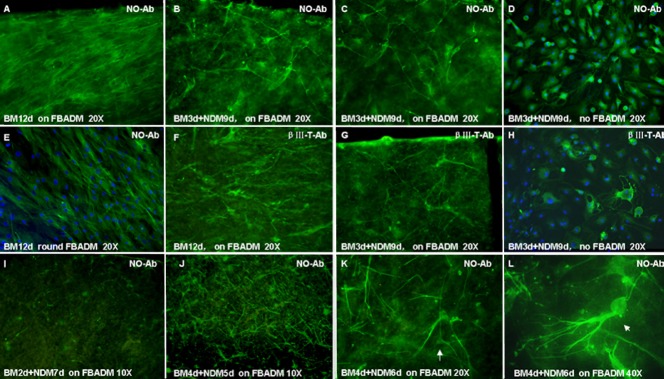
Cell morphology of BMSCs cultured with or without FBADM in induced or non-induced conditions (immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy).
(A–E, I–L) Neurite outgrowth primary antibody, marked as NO-Ab. (F–H) βIII tubulin primary antibody, marked as βIII-T Ab. (A, E, F) The BMSCs cultured on FBADM (A, F) and grown around FBADM (E) in basal medium (BM) for 12 days (non-induced) were parallel with long spindles. (B–D, G, H) The BMSCs cultured on FBADM (B, C, G) or without FBADM (D, H) in BM for 3 days and then induced in neural differentiation medium (NDM) for 9 days (induced, BM 3 d + NDM 9 d). (B, C) Some neurite outgrowth primary antibody-positive cells with bi/multipolar elongations formed a network-like structure on the surface of the FBADM, and they also appeared to express the neuron marker βIII tubulin (G). (I, J) In cells cultured for a total of 9 days, but in two different conditions, (BM 2 d + NDM 7d) or (BM 4 d + NDM 5 d), more neurite outgrowth-positive cells were found in the latter than in the former. (J) In the induced condition of (BM 4 d + NDM 5 d), the differentiated cells showed the morphology of unipolar and bipolar or multipolar neurons. (K, L) Induced in BM 4 d + NDM 6 d, the BMSCs differentiated into cells with the morphology of pyramidal cells (K, arrow, × 40) and cerebellum Purkinje's cells (L, arrow, × 40). These results suggest that BMSCs can differentiate into neuronal cells on FBADM after being induced in NDM for 5 to 6 days, and the differentiated neuronal cells can connect with each other via neurites to form a neural network-like structure. The FBADM can support the neuronal differentiation of BMSCs and the formation of a neural network-like structure. d: Days; NO-Ab: neurite outgrowth antibody; BMSCs: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; FBADM: fetal bovine acellular dermal matrix.
