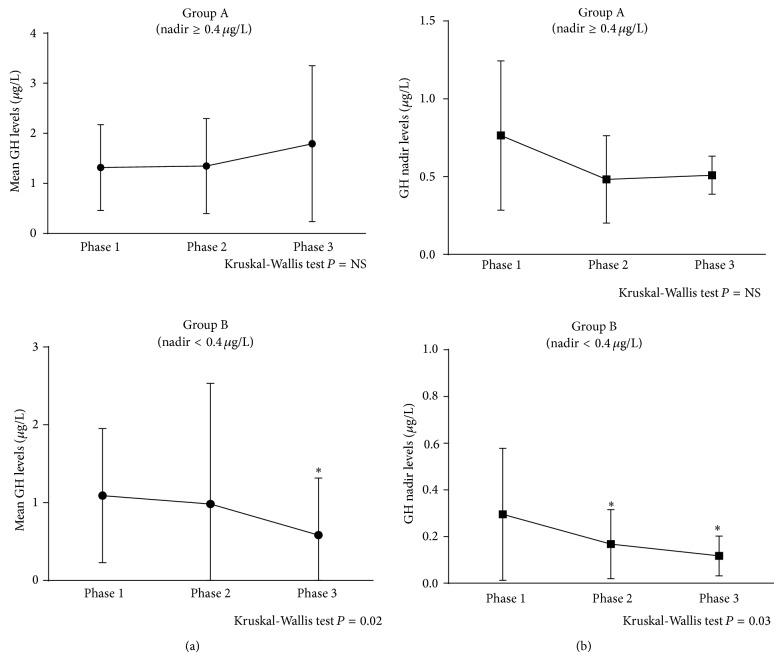
Figure 1.
(a) Mean GH levels in basal condition, evaluated as the mean of at least three consecutive samples, in patients of group A (i.e., GH nadir ≥ 0.4 mcg/L, upper) and group B (i.e., GH nadir < 0.4 mcg/L, lower). Patients of group B showed mean GH levels at long-term follow-up (phase 3) significantly lower than at the time of remission (phase 1), whereas no difference was observed in group A. * P < 0.05 versus phase 1. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. (b) Mean GH nadir, defined as the lowest GH value at any time after glucose administration (2 h-OGTT), in patients of group A (i.e., GH nadir ≥ 0.4 mcg/L, upper) and group B (i.e., GH nadir < 0.4 mcg/L, lower). Patients of group B showed mean GH nadir levels atlong-term follow-up (phase 3) and at the time of the last assessment available with the GH assay standardized to IS 80/505 (phase 2) significantly lower than at the time of remission (phase 1), whereas the decrease did not reach statistical significance in patients of group A. * P < 0.05 versus phase 1. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.