Figure 4. Structure–function analysis of the β1 integrin in uPAR/VN-induced cell spreading and signalling.
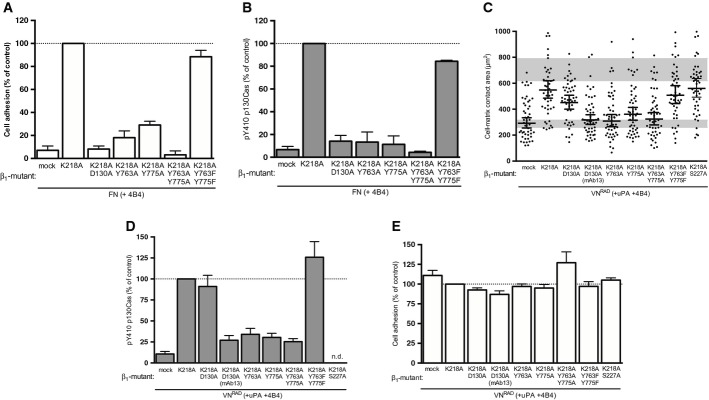
A, B Effect of β1 integrin mutants on canonical integrin-mediated FN adhesion and signalling. 293 cells co-expressing uPART54A and the indicated β1 variants were seeded on FN for 30 min. Cell adhesion (A) and p130Cas SD phosphorylation (B) were assayed and quantified. Adhesion is expressed in percentage of adhesion to PDL (n = 3, mean ± s.e.m.). The Western blot data are represented as percentage of phosphorylated p130Cas SD of β1K218A-expressing cells (n = 3, mean ± s.e.m.).
C–E Structural requirements for ligand-independent β1 integrin signalling and cell spreading. 293 cells co-expressing uPART54A and the indicated β1 variants were seeded on VNRAD in the presence of uPA and 4B4 for 30 min. Cell area (C), p130Cas SD phosphorylation (D) and cell adhesion (E) were assayed and quantified. Adhesion is shown in percentage of PDL (n = 3, means ± s.e.m.). The Western blot data are represented as percentage of phosphorylated p130Cas SD of β1K218A-expressing cells (n ≥ 3, mean ± s.e.m.). Cell-matrix contact area measurements represent at least 50 cells with indicated geometrical means ± 95% CI, in two independent experiments. The grey bars represent the range of cell area of not spread or fully spread uPART54A cells based on 95% CI on poly-D-lysine or on VN with uPA, respectively (Fig 2B).
