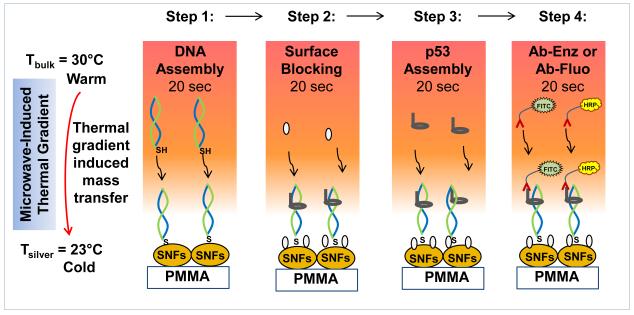
Fig. 1.
Schematic depiction of the working principle of microwave-accelerated bioassay (MAB) technique. In step 1, double-stranded and thiolated oligonucleotides are chemisorbed on to SNFs. In step 2, p53 protein binds to the double-stranded and thioated oligonucleotides and BSA binds to the surface of SNFs. In step 3, BSA is added to the surface to minimize the non-specific binding of proteins. In step 4, enzyme-modified antibody (Ab-Enz) or fluorophore-modified antibody (Ab-Fluo) binds the p53 on the surface of SNFs. Please note all unbound materials were washed away after each step. Temperature of bulk (Tbulk) and silver surface (Tsilver) is measured using fiber optic temperature sensors.