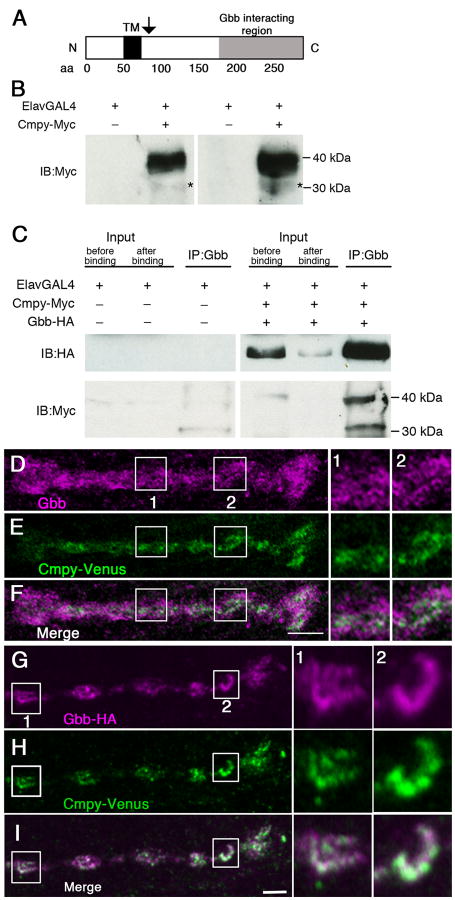
Figure 1. Crimpy and Gbb physically interact and colocalize in presynaptic terminals.
(A) Cmpy is a predicted Type II transmembrane protein. TM is the predicted transmembrane domain. Arrow indicates position of proposed proteolytic processing. (B) Two representative immunoblots of third instar ventral nerve cords (VNCs) from ElavGal4 or ElavGal4/UASCmpy-Myc animals. Left blot: 15 VNCs/lane; right blot: 25 VNCs/lane. Full-length Cmpy-Myc is 39 kDa; putative 31 kDa C-terminal Cmpy-Myc cleavage product (asterisk). (C) Co-immunoprecipitation of Gbb-HA and Cmpy-Myc from VNCs of the indicated genotypes. Mouse anti-Gbb antibody was used to immunoprecipitate Gbb-HA followed by Western blotting analysis using Rat anti-HA (top) and Rabbit anti-Myc (bottom) to detect Gbb and Cmpy, respectively. Proteins in the lysate prior to immunoprecipitation (5% of total input) are shown on the left before and after binding to anti-Gbb beads. Anti-Gbb co-immunoprecipitates full-length 39 kDa Cmpy-Myc and a 31 kDa Cmpy-Myc cleavage product. (D-F) Representative confocal images of boutons at NMJ4 of D42Gal4, UASCmpy-Venus larvae stained with anti-Gbb (D) and anti-GFP (E) with the channels merged in (F). Boxes (1) and (2) are magnified to the right of panels (D-F) to demonstrate co-localization of Cmpy-Venus (anti-GFP) and Gbb (anti-Gbb). (G-I) Representative confocal images of boutons at NMJ4 of UASGbb-HA; D42Gal4/UASCmpy-Venus larvae stained with anti-HA (G) and anti-GFP (H) with the channels merged in (I). Boxes (1) and (2) are magnified to the right of panels (G-I) to demonstrate co-localization of Cmpy-Venus (anti-GFP) and Gbb-HA (anti-HA). Scale bars are 2 μm.