Figure 3. Crimpy traffics Gbb to dense core vesicles.
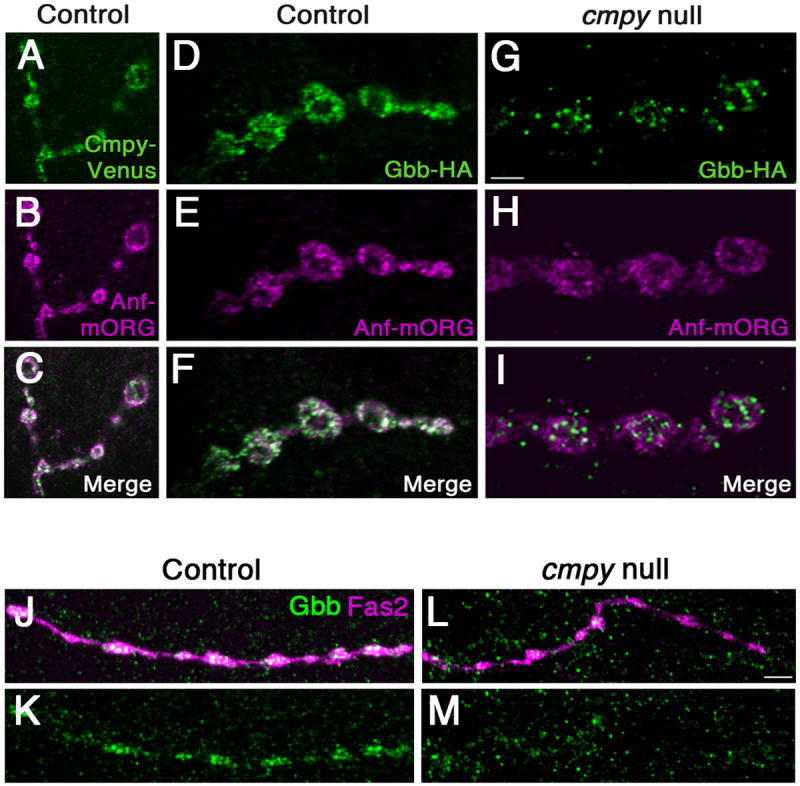
(A-C) Representative confocal images of boutons at NMJ4 of D42Gal4, UASCmpy-Venus/UASAnf-mOrange larvae stained with anti-GFP (A), anti-RFP (B), and merged in (C) demonstrate association of Cmpy-Venus (anti-GFP) with Anf-mOrange/DCVs (anti-RFP) in presynaptic terminals. (D-I) Representative confocal images of boutons at NMJ4 in larvae with Gbb-HA, Anf-mOrange expressed via D42Gal4 in an otherwise wild-type background (D-F) and in a cmpyΔ8 background (G-I) stained with anti-HA (Gbb-HA) and anti-RFP (Anf-mOrange/DCVs). In an otherwise wild-type background, Gbb-HA and Anf-mOrange display extensive co-localization. In cmpyΔ8 mutants, presynaptic Gbb-HA does not exhibit appreciable co-localization with Anf-mOrange. (J-M) Representative confocal images of type III boutons on muscle 12 in larvae with Anf-mOrange expressed via D42Gal4 in an otherwise wild-type background (J,K) and in a cmpyΔ8 background (L,M) stained with anti-Gbb (Gbb) and Fas2 (neuronal membrane). In an otherwise wild-type background, Gbb strongly localizes to type III boutons. In cmpyΔ8 mutants, Gbb does not exhibit appreciable localization in type III boutons. Scale bars are 2 μm.
