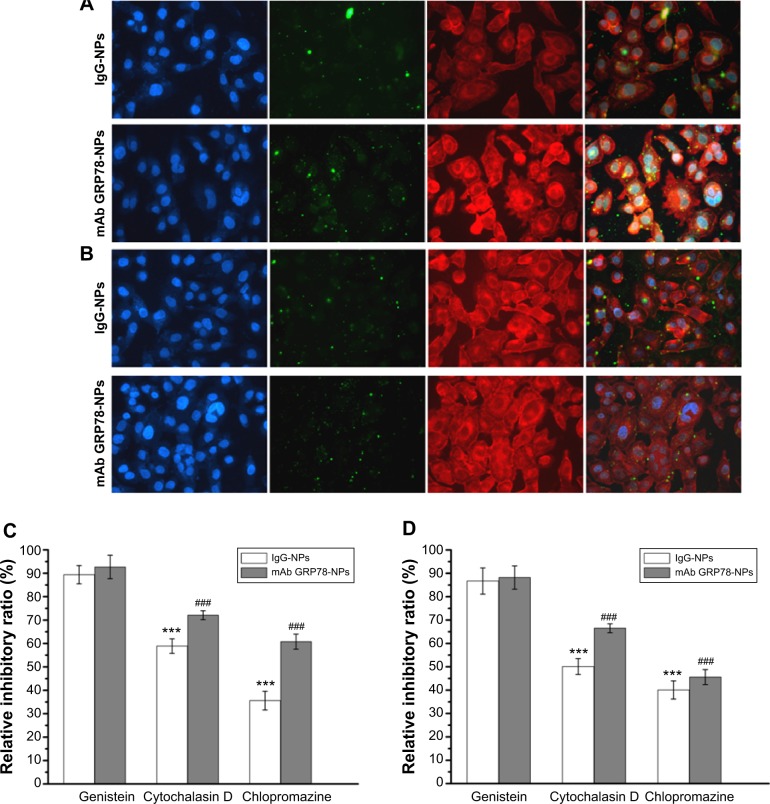
Figure 4.
mAb GRP78-NPs could effectively enhance drug accumulation in cells highly expressing GRP78.
Notes: Confocal images of (A) SMMC-7721 and (B) PLC cells after incubation for 6 hours with mAb GRP78-NPs and isotype IgG-NPs. The nucleus was stained with Hoechst (blue) for 15 minutes at 37°C and all NPs were labeled by FITC (green). The cytoskeleton was stained by TRITC-labeled phalloidin. (C) Effects of endocytic inhibitors on the uptaking ability of the two NPs in SMMC-7721 cells. ***P<0.001 versus the IgG group treated with genistein. ###P<0.001 versus the mAb GRP78 group treated with genistein. (D) Effects of endocytic inhibitors on the uptaking ability of the two NPs in PLC cells. ***P<0.001 versus the IgG group treated with genistein. ###P<0.001 versus the mAb GRP78 group treated with genistein. Blocking by using cytochalasin D or chlorpromazine could inhibit the obviously internalizing effect of both NPs. Conversely, addition of genistein into both cells seemed to have little effect on the uptake of either NP.
Abbreviations: FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; IgG-NPs, NPs conjugated with IgG; NP, nanoparticle; mAb GRP78, monoclonal antibody against GRP78; mAb GRP78-NPs, NPs conjugated with mAb GRP78; SD, standard deviation; TRITC, tetramethylrhodamine.