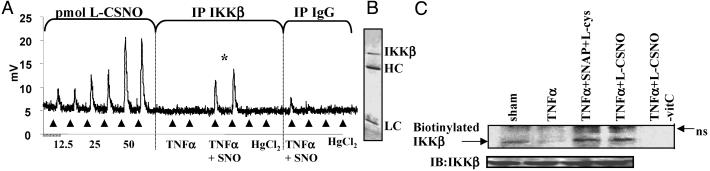
Fig. 3.
S-nitrosylation of IKKβ. (A) Jurkat T cells were treated with 1 mM l-CSNO for 30 min and subsequently with TNFα for 10 min. IKKβ was immunoprecipitated from lysates containing 2.2 mg of protein by using an IKKβ antibody. A control immunoprecipitation was performed by using an isotype-matched Ig (IgG). After immunoprecipitation, selected samples were treated with HgCl2, and all samples were treated with sulfanilamide to ensure specificity. S-nitrosylation of IKKβ was assessed by chemiluminescence. *, P < 0.05 (Student's t test) compared with NO signal obtained in the TNFα + l-CSNO subjected to immunoprecipitation with the IgG control antibody. (B) IKKβ was immunoprecipitated from untreated Jurkat T cells, samples boiled in sample buffer, separated on SDS/PAGE gel, and silver stained. The location of IKKβ is indicated. HC, antibody heavy chain; LC, antibody light chain. (C) Cells were treated as in A, and lysates were subjected to biotin derivatization. Biotinylation of IKKβ was detected after immunoprecipitation of the IKKβ-containing complex and Western blotting using streptavidin–horseradish peroxidase. In control samples, reduction by ascorbate (–vitC) was omitted. IB, anti-IKKβ immunoblot; ns, nonspecific reactivity.