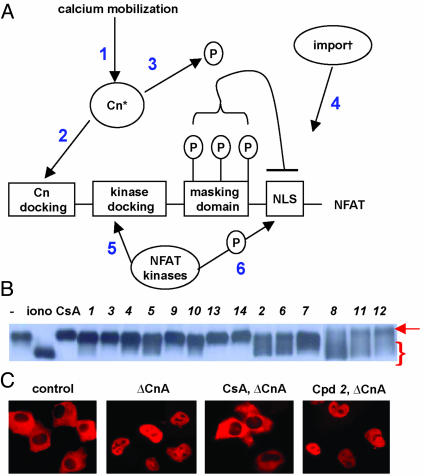
Fig. 2.
Small molecule inhibitors act upstream of calcineurin to block NFAT import. (A) A schematic of NFATc3 depicting the functional domains of the N terminus that regulate calcium-activated nuclear import and important regulatory sites. 1 refers to calcium mobilization as well as calmodulin activation, 2 to calcineurin docking the N terminus of NFAT, 3 to the phosphatase activity of calcineurin, 4 to the nuclear import proteins that recognize nuclear location signals, and 5 and 6 to the docking and activation of NFAT kinases that oppose calcineurin. (B) Western blot of NFATc3 from BHK cells treated for 45 min with carrier alone, ionomycin, or ionomycin together with one of the NFATc3 nuclear import inhibitors. The control cells show NFATc3 with the lowest mobility (arrow), whereas cells treated with ionomycin show the highest mobility (brackets). All compounds were used at concentrations that block all detectable nuclear import. (C) Effect of NFAT inhibitors on intracellular calcineurin activity. (Left to right) NFATc3 cytoplasmic localization in control BHK cells, nuclear location of NFATc3 in cells coexpressing ΔCnA, cytoplasmic localization of NFATc3 in cells coexpressing ΔCnA and treated with 1 μM CsA, nuclear localization of NFATc3 in cells coexpressing ΔCnA and treated with compound 2.