Fig. 2.
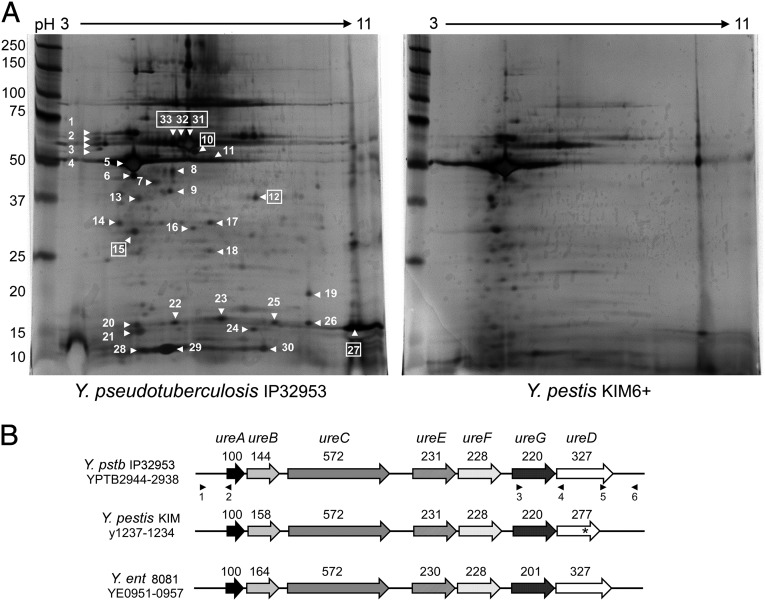
Urease proteins are present in the toxic subfraction of Y. pseudotuberculosis. (A) Silver-stained 2-DE gels of the membrane supernatant subfraction of Y. pseudotuberculosis and Y. pestis. The numbered spots indicate proteins that were identified as being absent, differentially produced, or with a different pI in Y. pestis compared with Y. pseudotuberculosis profile; boxed numbers indicate urease subunits (Table S1). Molecular mass standards are shown on the left. (B) Organization of the urease cluster in Y. pseudotuberculosis (Y. pstb) IP32953, Y. pestis KIM, and Y. enterocolitica (Y. ent) 8081. The urease locus has a conserved organization in the three species and contains all seven genes that encode the structural (UreABC) and accessory (UreEFGD) proteins of the multimeric urease enzyme. The ureD gene in Y. pestis is a pseudogene (*). The predicted number of amino acids for each protein is noted above the corresponding gene. The positions of primers used for mutagenesis and complementation are indicated by numbered black triangles (identified in Table S2).