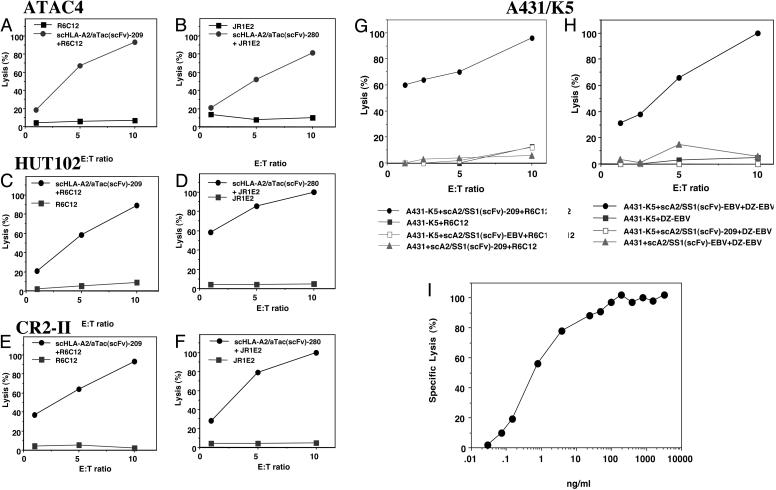
Fig. 3.
Potentiation of CTL-mediated lysis of HLA-A2-negative tumor cells by the scHLA-A2/scFv fusion molecule. CD25-transfected ATAC4 or CD25-positive leukemic HLA-A2-negative cells coated or not coated with the scHLA-A2/aTac(scFv) fusion molecule folded around the G9-209M (A, C, and E) or G9-280V (B, D, and F) gp100-derived peptides were incubated with melanoma-reactive gp100-peptide-specific CTL clones R6C12 or JR1E2, respectively, in a [35S]methionine release assay. Mesothelin-expressing A431/K5 cells were coated or not coated with a scHLA-A2/SS1(scFv) fusion molecule folded around the gp100-derived G9-209M peptide (G) or EBV peptide (H) and incubated with the R6C12 G9-209M-specific CTL clone or EBV-specific line, respectively. A431/K5 cells incubated with scHLA-A2/SS1(scFv) folded around the EBV (G) or G9-209M (H) peptides were not killed by R6C12 G9-209M-specific CTLs or DZ/EBV EBV-specific CTLs, respectively. Insensitivity of scHLA-A2/SS1(scFv)-coated A431 cells is also shown as the control. (I) Dose-dependent activity of the scHLA-A2/SS1(scFv) molecule folded around the EBV peptide on A431/K5 cells using EBV-specific CTLs.