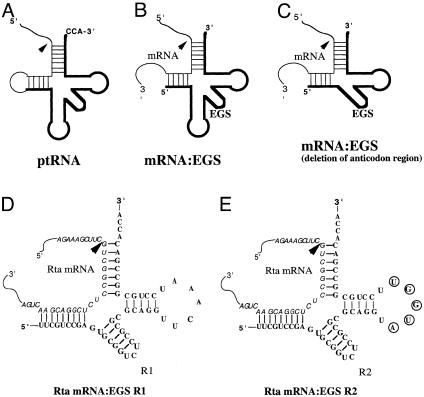
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of substrates for RNase P. (A) A natural substrate precursor tRNA for RNase P. (B and C) Hybridized complex of a target RNA (e.g., mRNA) and an EGS that resembles the structure of a tRNA and can be cleaved by RNase P. C results from B by deletion of the anticodon domain of the EGS, which is dispensable for EGS-targeting activity (21). Arrowheads indicate the site of cleavage by RNase P. (D and E) Complexes between the Rta mRNA sequence and EGS R1 and R2, respectively. The sequence of these EGSs equivalent to the tRNA sequence was derived from tRNAser and resembles the T-stem and loop and a variable region of the tRNA molecule.