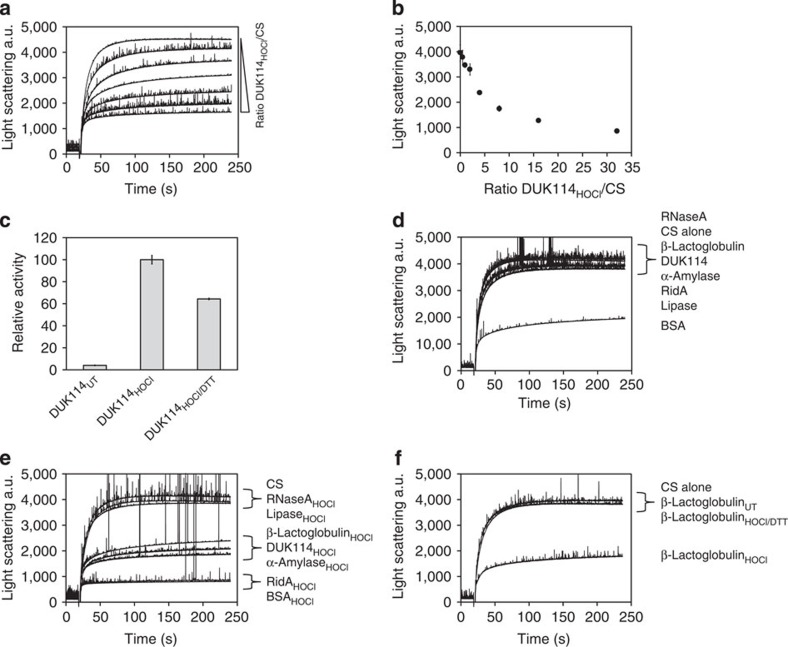
Figure 9. HOCl induces chaperone activity in homologues to RidA and unrelated proteins.
(a,b) The Drosophila melanogaster RidA homologue DUK114 was purified and subjected to chaperone assays. Inhibition of citrate synthase aggregation strongly depends on the ratio of DUK114HOCl over citrate synthase similar to RidAHOCl and other unrelated proteins. (c) In contrast to RidAHOCl (and β-lactoglobulin; see also f), activation of DUK114HOCl is only partially reversible by DTT. (d,e) In addition to DUK114, a number of other proteins was tested for HOCl-induced chaperone activity. RNaseA and lipase are unaffected by HOCl treatment, whereas β-lactoglobulin, α-amylase and BSA show HOCl-inducible chaperone activity. BSA is already active before treatment (d). (f) Activation of β-lactoglobulin is reversible by DTT. Representative measurements are shown for a,d,e and f. Data represented in b and c are the means of three independent measurements.