Table 4.
Area Under the Receiver-Operating Characteristic Curve, Optimal Cutoff Points, and Validity Parameters Predicting Obesity-Related Disease in Females
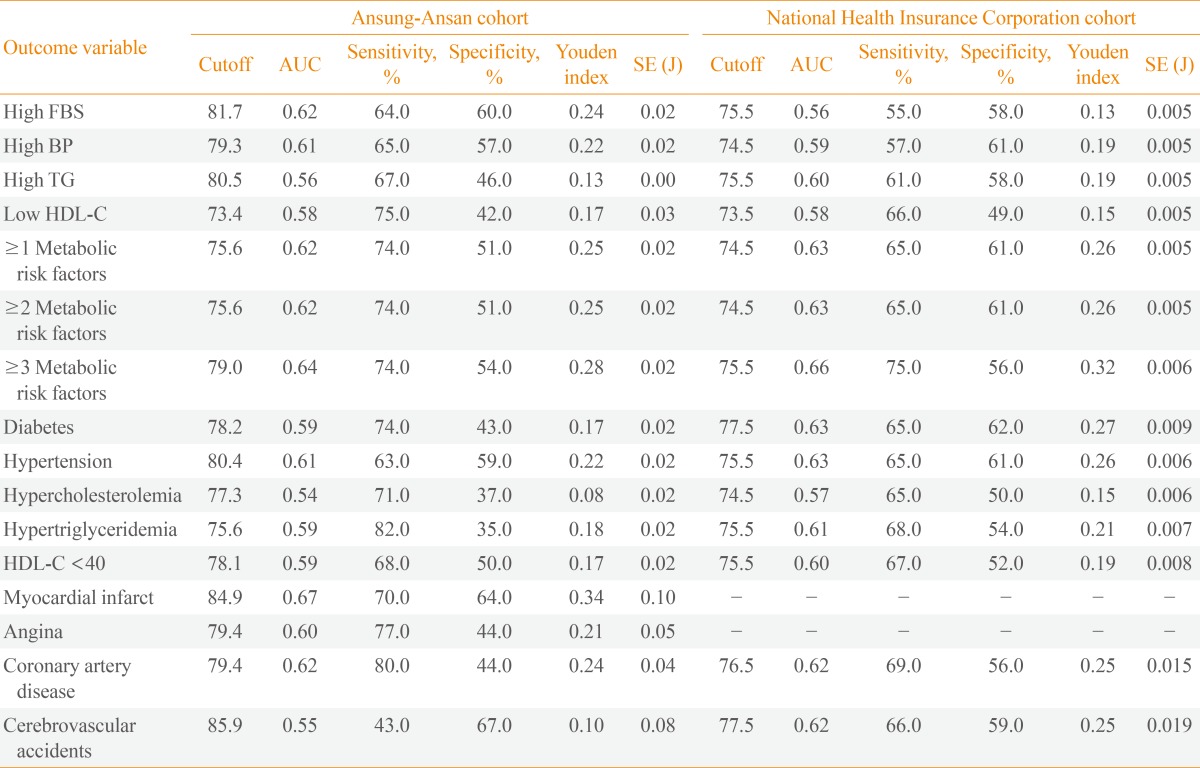
High fasting blood sugar (FBS) was diagnosed when the FBS was ≥100 mg/dL or the subjects were receiving glucose-lowering medications. High blood pressure (BP) was diagnosed when the systolic BP was ≥130 mm Hg, diastolic BP was ≥85 mm Hg, or the subjects were receiving antihypertensive medications. High triglycerides (TG) were diagnosed when the TG level was ≥150 mg/dL. Low high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) was diagnosed when the HDL-C level was <50 mg/dL. Metabolic risk factors included high BP, high FBS, high TG, and low HDL-C of the modified National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III criteria other than waist circumference. Hypertension was diagnosed when the systolic BP was ≥140 mm Hg, diastolic BP was ≥90 mm Hg, or the subjects were receiving antihypertensive medications. Diabetes was diagnosed when the FBS was ≥100 mg/dL, 2-hour postprandial blood sugar was ≥200 mg/dL, or the subjects were receiving glucose-lowering medications. Hypercholesterolemia was diagnosed when the total cholesterol was ≥200 mg/dL. Hypertriglyceridemia was diagnosed when the TG was ≥200 mg/dL.
AUC, area under the curve; SE, standard error.
