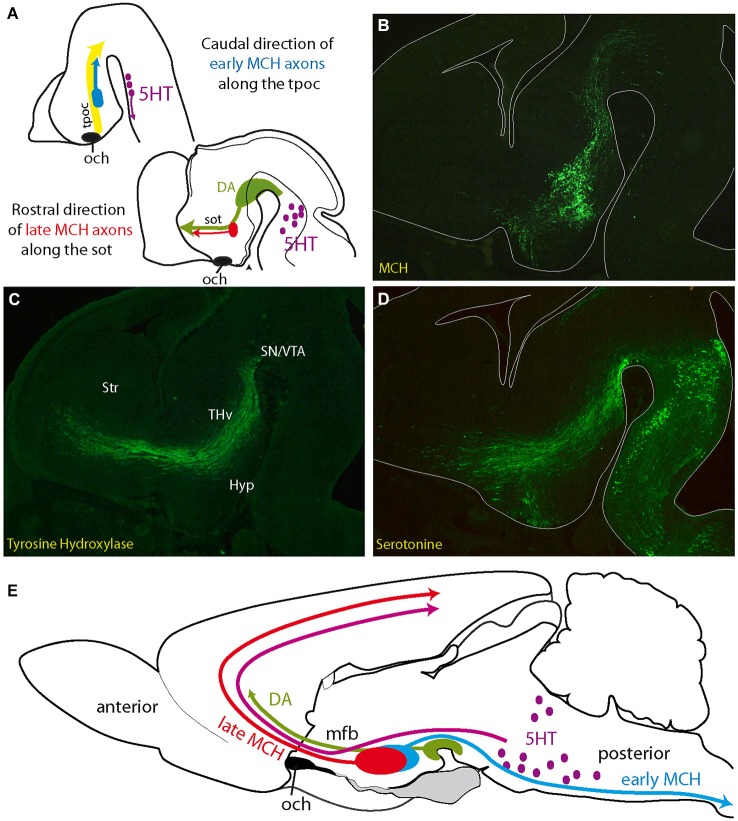
Figure 3.
(A) Initial projections of MCH expressing neurons follow pioneer tracts, but their direction changes as the embryo matures. Axons of first generated MCH expressing neurons follow the tpoc toward the midbrain. Axons from late generated MCH expressing neurons follow the sot toward the telencephalon, along DA and 5HT axons (see Croizier et al., 2011). (B–D) Distribution of serotonin, MCH (MCH-GFP, revealed with an anti-GFP antibody; see Croizier et al., 2011) and tyrosine hydroxylase (dopamine) in three adjacent sections cut in the parasagittal plane and passing through the mfb of an E14 mouse embryonic brain. Serotonergic and dopaminergic axons from respectively the hindbrain and midbrain travel along the tpoc and arch rostrally at the level of the posterior hypothalamus, where MCH expressing cells are found. Note the pattern of serotonergic axons that closely follows the inverted Y pattern of the sot/tpoc. (E) Schematic illustration of the ascending serotonergic and dopaminergic pathways to the telencephalon through the mfb and the distribution patterns of early and late MCH projections in the adult rat central nervous system. Abbreviations: DA: dopaminergic neurons; Hyp: hypothalamus; MCH: melano-concentrating hormone containing neurons; mfb: medial forebrain bundle; och: optic chiasm (or presumptive position of the optic tract in A); SN: substantia nigra; sot: supraoptic tract; Str: presumptive striatal region; THv: ventral thalamic region; tpoc: tractus postopticus; VTA: ventral tegmental area (presumptive); 5HT: serotonergic neurons.