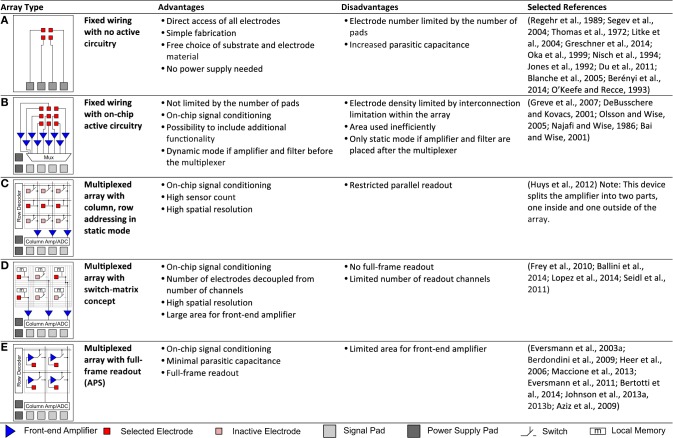
Figure 3.
Array architectures. This table summarizes and classifies the different architectures that are typically used for MEAs. Advantages, disadvantages are stated and representative selected references given. (A,B) Fixed wiring. (A) Electrodes are directly connected to signal pads with no active circuitry. (B) Electrodes are directly connected to on-chip active circuitry for signal conditioning. (C–E) Multiplexed arrays. (C) Signals are multiplexed to the signal pads via column, row addressing in static mode. (D) More flexible addressing is achieved by adding more routing resources within the array in the switch-matrix mode. (E) All electrodes can be sampled at fast speeds in full-frame readout implemented in active pixel sensor (APS) MEAs.