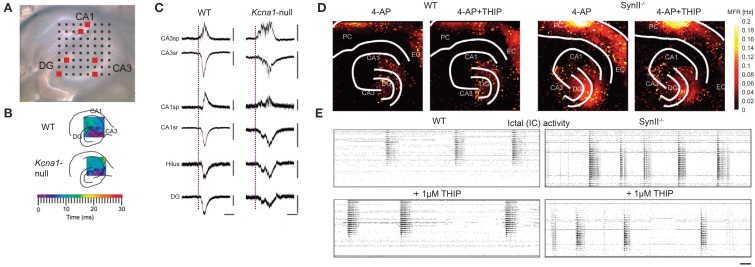
Figure 9.
Waves in acute hippocampal slices revealed by MEAs. (A–C) Studying the effect of the delayed rectifier potassium channel α-subunit Kv1.1 to sharp waves in in vitro hippocampal slices using MEAs, modified with permission from Simeone et al. (2013). (A) Image of a Kcna1-null (knock-out of the gene encoding Kv1.1) hippocampal slice on an MEA. Black squares correspond to the electrodes. The regions of the hippocampus are also indicated. (B) The sharp waves in wild-type (WT) and Kcna1-null hippocampi are initiated in CA3 that spread with similar time-courses. (C) Representative sharp waves from WT and Kcna1-null hippocampi recorded at the location of red boxes in (A). The sharp waves are longer (with ripples) in Kcna1-null compared to WT. Scale bars: horizontal, 50 ms; vertical, 50 μV except for WT CA3sp (100 μV), WT CA3sr (200 μV), KO CA1sp (20 μV), and WT CA1sr (200 μV). CA, cornus ammonis; DG, dentate gyrus. (D,E) Studying the effect of deleting synapsin II (Syn II) to the tonic inhibition in mouse hippocampal slices using HDMEAs, adapted with permission from Medrihan et al. (2014). (D) Mean firing rate computed from each electrode from WT and Syn II knock-out hippocampal slices before and after THIP treatment. THIP: (4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-3-ol; gaboxadol), a selective agonist of δ subunit-containing GABAA receptors. (E) Raster plots showing highly synchronized bursts, x-axis corresponds to time, y-axis corresponds to pixels (electrode). THIP reduced the high frequency bursts in Syn II knock-out hippocampus. Scale bar: 1 min.