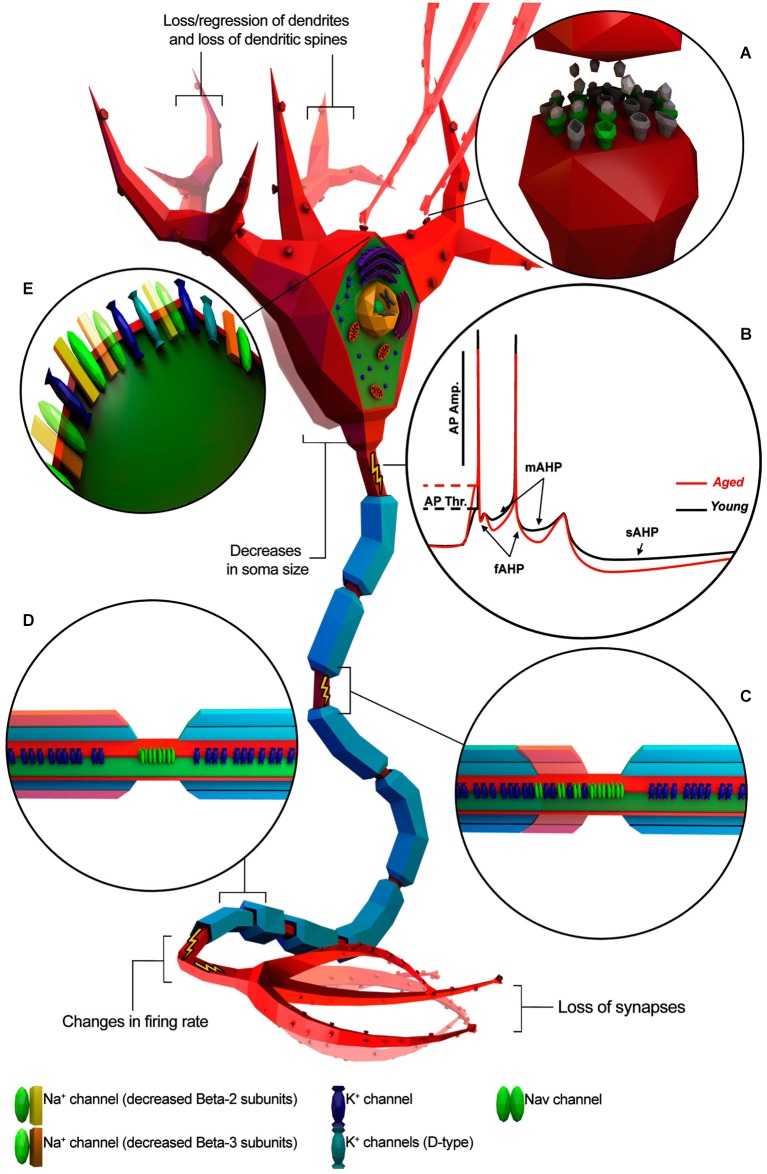
Figure 1.
Known age-related electrophysiological and morphological changes in neurons. Neuron is depicted as a generic myelinated neuron for simplicity, in order to summarize information from different animal models and neuronal cell type. (A) Age-related increase of altered neurotransmitter receptors (gray) and decreased expression of normal ones (green). (B) Representative AP traces of young and aged neuron. (C) Absence/disruption of paranodal ultrastructure (in red) leading K+ channels to be relocated adjacent to “Nav” clusters. (D) Depletion of myelin layers (in red) leading to an increase of the occurrence of redundant myelin sheaths exposing the enclosed axon. (E) Alterations in Na+ and K+ channel properties or subtype expression patterns. (Illustration was created using Autodesk 3Ds Max and Adobe Photoshop).