Figure 9.
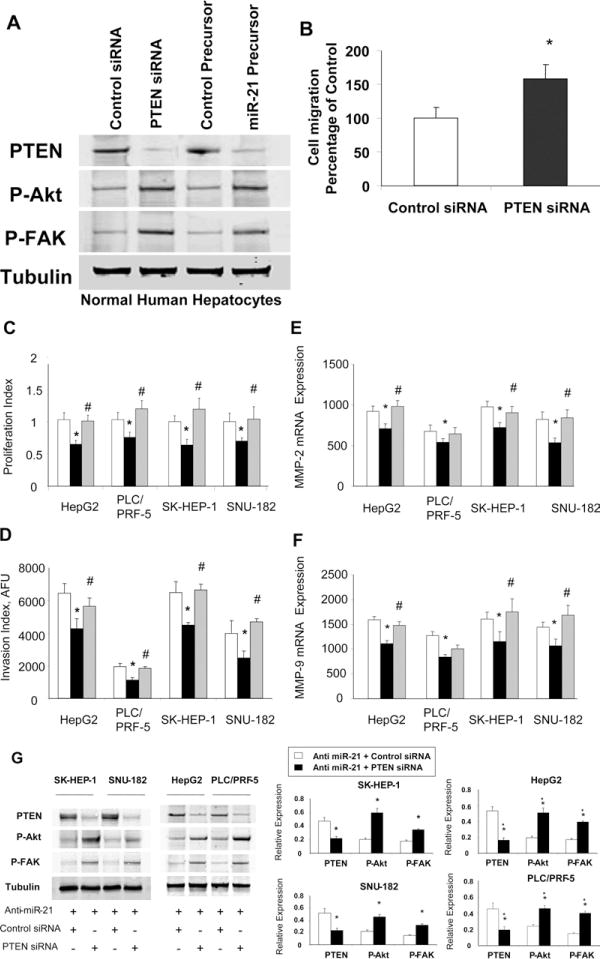
Down-regulation of PTEN attenuates the effects of anti–miR-21 on HCC cell growth and invasion. (A) Nonmalignant human hepatocytes were transfected with control or PTEN siRNA, or control or miR-21 precursor and immunoblot analysis for PTEN, phospho-Akt Ser(P)473, phospho-FAKTyr(P)516/517, and tubulin were performed. (B) Cell migration was assessed in human hepatocytes incubated with control or PTEN miRNA. (C–F) HCC cells (5 × 104/well) in 96-well plates were cotransfected with either siRNA to PTEN or control siRNA, along with 30 nmol/L anti-miR-21. (□, control anti-miRNA + control siRNA; ■, anti-miR-21 + control siRNA; grey bars, anti–miR-21 + PTEN siRNA). (C) Cell proliferation or (D) invasion was assessed after 72 hours as described in the Materials and Methods section. The mean and standard error from 4 separate experiments are shown. mRNA expression of (E) MMP-2 and (F) MMP-9 were quantitated by real-time PCR, and expressed relative to that of β-actin mRNA concurrently assessed in the same samples. (G) Cells were cotransfected with anti–mir-21 and either control or PTEN siRNA. Immunoblot analysis of PTEN, phospho-Akt Ser(P)473, and phospho-FAK Tyr(P)516/517, and tubulin was performed. Representative immunoblots are shown along with quantitative data that show the mean ± standard error from 4 separate blots. *P < .05 when compared with control siRNA-transfected cells.
