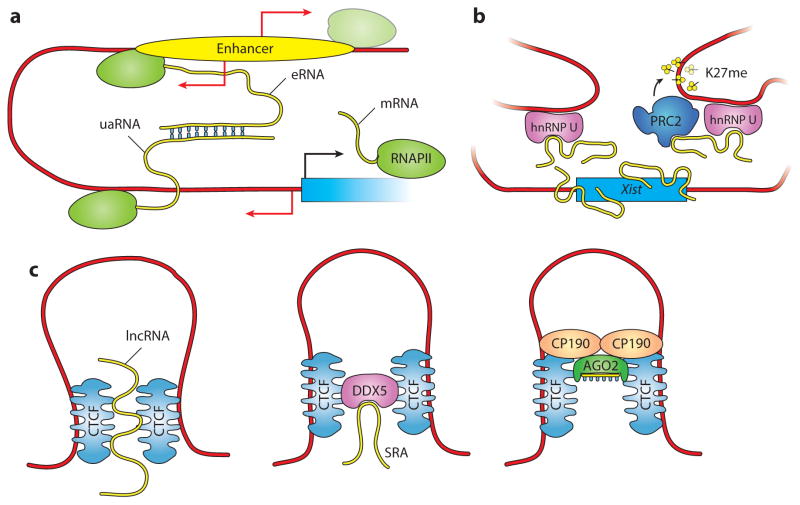
Figure 4.
Potential roles of lncRNAs (long noncoding RNAs) in nuclear organization. (a) In this speculative model, eRNAs (enhancer RNAs) mediate enhancer-promoter communication directly via base-pair interactions with uaRNAs (upstream antisense RNAs) and possibly facilitate chromatin looping. (b) The lncRNA Xist utilizes the three-dimensional organization of chromatin to spread its silencing activity over the whole X chromosome. Interactions with chromatin might be mediated via the matrix protein hnRNP U (41). At the target sites, Xist facilitates H3K27me3 deposition via PRC2 recruitment (187). (c) Roles of ncRNAs (noncoding RNAs) in CTCF function. (Left) Human CTCF binds RNA directly and RNA interactions mediate multimerization, which might guide chromatin looping and organization (141). (Middle) Human CTCF also binds RNA indirectly through its interactions with the RNA helicase DDX5, here bound to the lncRNA SRA (182). (Right) Drosophila CTCF and CP190 insulator proteins interact physically and genetically with AGO2, a small ncRNA-binding protein and key component of the RNAi machinery (92, 116).