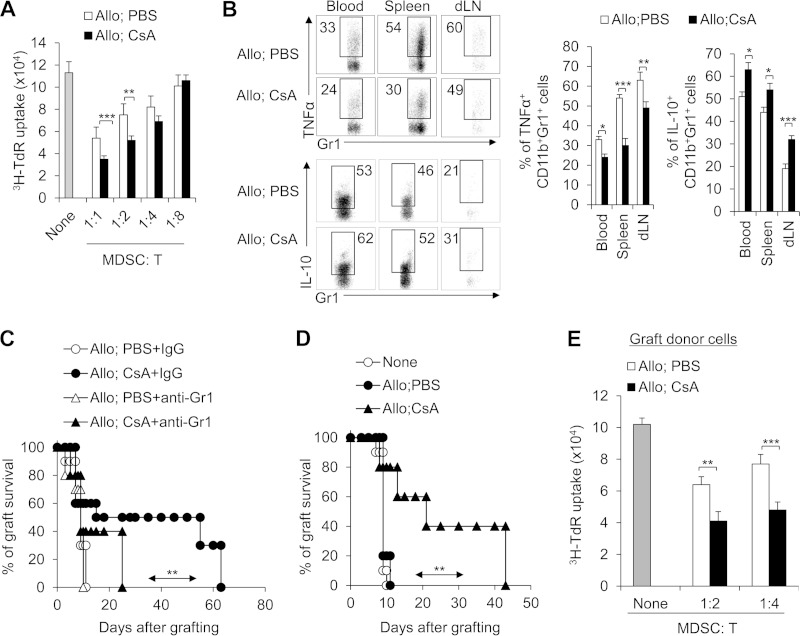
FIG 4.
CD11b+ Gr1+ MDSCs are required for CsA-prolonged allograft survival. (A) The suppressive activities of myeloid-derived CD11b+ Gr1+ cells were analyzed in vitro. The splenic CD11b+ Gr1+ cells treated with CsA in the allograft recipient mice showed increased suppressive activity. The ratio of MDSCs to T cells is shown below the graph. T cells were stimulated with allogeneic BALB/c splenocytes in the presence of splenic CD11b+ Gr1+ cells that were isolated from the allograft recipient mice. T cell proliferation was determined by [3H]thymidine (3H-TdR) incorporation. (B) TNF-α and IL-10 expression in splenic CD11b+ Gr1+ cells was analyzed by intracellular staining. A typical FCM figure is shown, and the data are summarized in the two graphs to the right of the FCM figure. (C) Depleting Gr1+ cells in CsA-treated allograft recipient mice with a MAb (RB6-8C5) resulted in severe allograft rejection responses in the recipient mice (n = 10). (D and E) Adoptive transfer of CD11b+ Gr1+ (CD8−) cells from CsA-treated allograft recipient mice significantly prolonged allograft survival (n = 10). The C57BL/6 recipient first underwent transplantation, and on days 7 and 8, a total of 1 × 106 CD11b+ Gr1+ cells were sorted from the spleens of CsA-treated or PBS-treated control mice and transferred into the C57BL/6 recipient mice via i.v. injection. After 10 to 12 h, both groups underwent allograft skin transplantation and the graft survival curve was plotted (n = 10) (D), and on days 7 and 8 after allograft skin transplantation, the local graft infiltrating donor CD45.1+ CD11b+ Gr1+ cells were isolated and their suppressive activities were analyzed in vitro (E). The data are representative of three (A and B) or two (C and D) independent experiments (for panels A, B, and E, n = 4 or 5). Values that are statistically significantly different are indicated by bars (or an arrow) and asterisks as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.