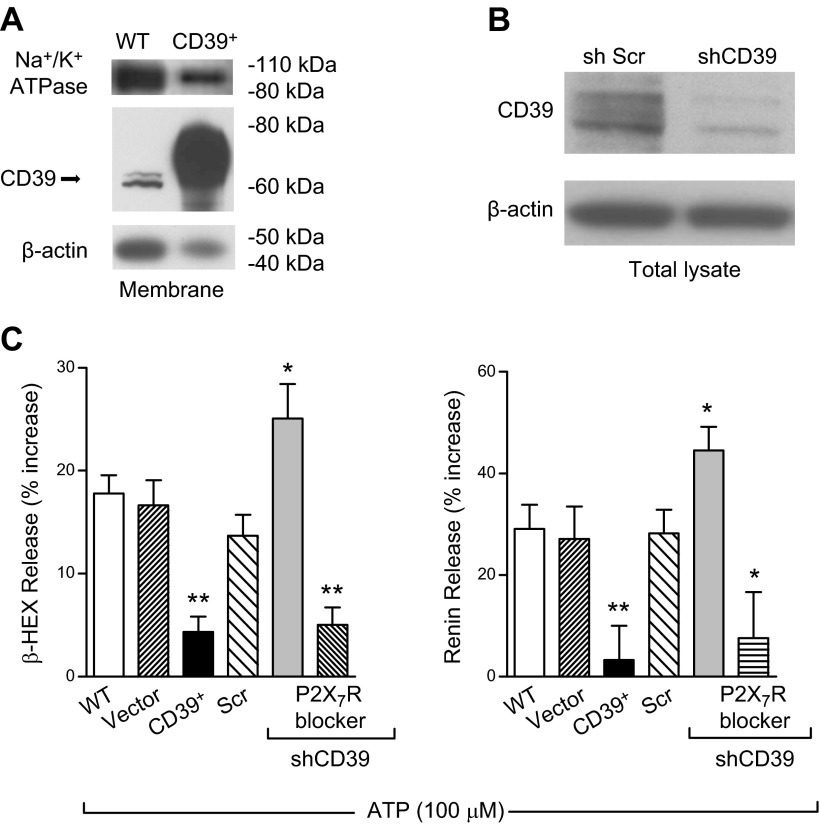
Figure 2.
CD39 expression modulates ATP-induced MC degranulation and renin release in HMC-1 cells. A) Representative Western blot of membrane fractions, prepared from WT and CD39-overexpressing (CD39+) HMC-1, probed with anti-CD39, anti-β-actin, and anti-Na+/K+ ATPase (membrane fraction marker, 40 and 5 μg/lane for WT and CD39+ cells, respectively). B) Western blot of HMC-1 total lysates transduced with lentivirus carrying sh scrambled (Scr) or shCD39 probed with anti-CD39 and anti-β-actin (50 μg/lane). C) ATP-induced degranulation and renin release are markedly reduced in CD39-overexpressing HMC-1. In contrast, the silencing of CD39 enhances degranulation and renin release. WT HMC-1 and HMC-1 infected with empty vector (Vector), CD39-overexpressing vector (CD39+), lentivirus carrying sh scrambled, and sh-silenced CD39 (shCD39) were incubated with ATP (100 μM) for 20 min in the absence or presence of A740003 (P2X7R blocker; 3 μM, 15 min preincubation); β-HEX and renin content was measured in the supernatants at the end of the incubation. Basal β-HEX release was 2.27 ± 0.30% (n = 22), and basal renin release (angiotensin I formed) was 3.20 ± 0.75 ng/h/mg protein (n = 17). Bars are means ± sem (n = 4–28). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. WT cells by unpaired t-test.