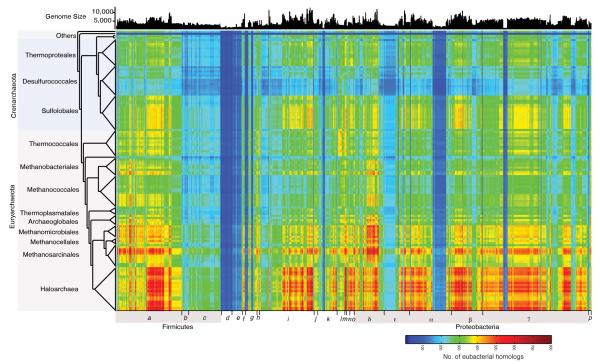
Extended Data Figure 1. Inter-domain gene sharing network.
Each cell in the matrix indicates the number of genes (e-value ≤10−10 and ≥25% global identity) shared between 134 archaeal and 1,847 bacterial genomes in each pairwise inter-domain comparison (scale bar at lower right). Archaeal genomes are listed as in Fig. 1. Bacterial genomes are presented in 23 groups corresponding to phylum or class in the Genbank nomenclature: a = Clostridia; b = Erysipelotrichi, Negativicutes; c = Bacilli; d = Firmicutes; e = Chlamydia; f = Verrucomicrobia, Planctomycete; g = Spirochaete; h = Gemmatimonadetes, Synergisteles, Elusimicrobia, Dyctyoglomi, Nitrospirae; i = Actinobacteria; j = Fibrobacter, Chlorobi; k = Bacteroidetes; l = Fusobacteria; Thermatogae, Aquificae, Chloroflexi; m = Deinococcus-Thermus; n = Cyanobacteria; o = Acidobacteria; δ,ε,α,β,γ = Delta, Epsilon, Alpha, Beta and Gamma proteobacteria; p = Thermosulfurobateria, Caldiserica, Chysiogenete, Ignavibacteria. Bacterial genome size in number of proteins is indicated at top.