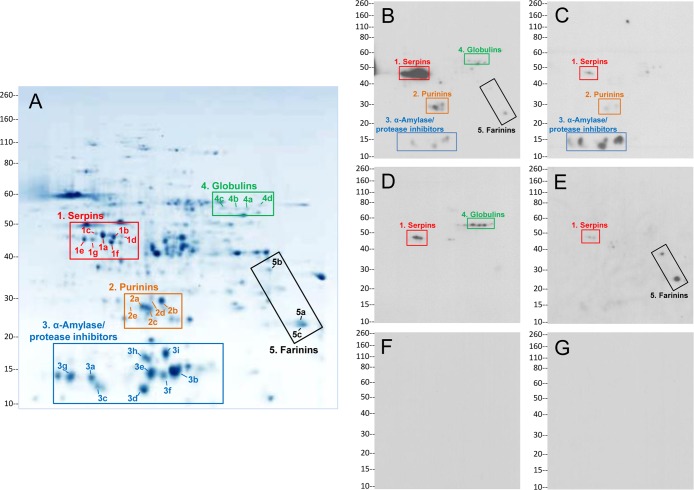
Figure 3.
Identification of specific nongluten proteins targeted by antibody response in celiac disease. (A) Pattern of proteins of the nongluten extract after separation by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and Coomassie staining. Numbered spots refer to proteins identified as antibody targets in patients. Proteins in five groups, shown in boxes, were found to be the main nongluten antigen targets of the antibody response: serpins, purinins, α-amylase/protease inhibitors, globulins, and farinins. Group numbers correspond to those in Table 1. Individual protein spot numbers correspond to those in Table 2. (B–E) Immunoblots showing serum antibody reactivity to the two-dimensionally separated proteins in representative patients and healthy controls: (B) IgG reactivity to serpins, purinins, α-amylase/protease inhibitors, globulins, and farinins in a patient with celiac disease; (C) IgG reactivity to serpins, purinins, and α-amylase/protease inhibitors in a patient with celiac disease; (D) IgG reactivity to serpins and globulins in a patient with dermatitis herpetiformis; (E) IgA reactivity to serpins and farinins in a patient with dermatitis herpetiformis; (F) IgG and (G) IgA reactivity in healthy controls, indicating lack of binding to nongluten proteins. Molecular weight markers (in kDa) are shown to the left of each panel.