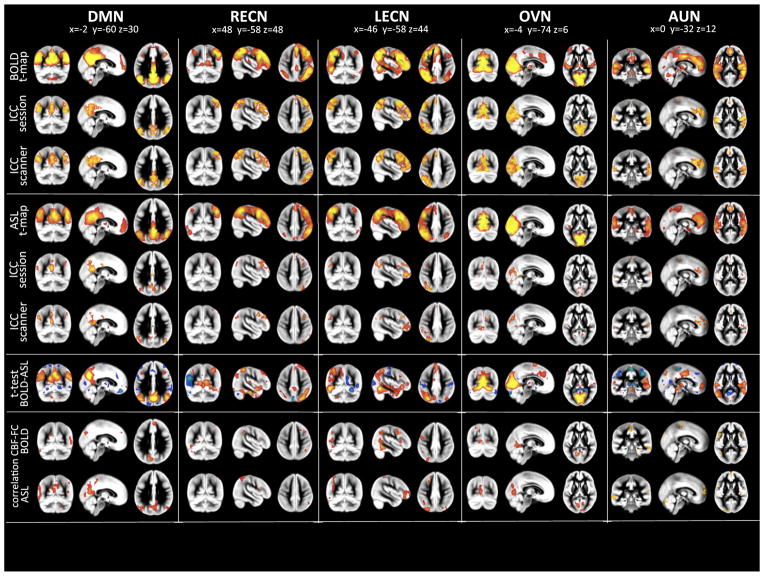
Fig. 3.
Results from joint-ICAs for BOLD and ASL (Display, organization and color-scaling are analog to Fig. 2). Modality specific group RBNs were computed as one-sample t-test across the specific single subject maps. Left column displays BOLD RBN results while right column those for pCASL. Five common RBNs were analyzed: Default Mode Network (DMN), left and right Executive Control Networks (L/R-ECNs), Occipital Visual Network (OVN) and Auditory Network (AUN). Test–retest reliability for session and scanner are displayed as Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) maps for BOLD and ASL networks (ICC maps were masked by ICA group RBN maps thresholded at z > 2). Differences between the two modalities (BOLD vs. ASL) were assessed by means of two-sample two-sided t-tests (significance threshold was set at p < 0.001). The bottom row displays voxel-wise correlation maps for CBF and Functional Connectivity strength (z-scores) for the five distinct networks (only significant (p < 0.05) correlations above r > 0.4 are displayed. Correlation maps have been masked by ICA group RBN maps thresholded at z > 2). Multi-slice views of all analyses can be found in Supplemental Figs. S1–S5.