FIGURE 1.
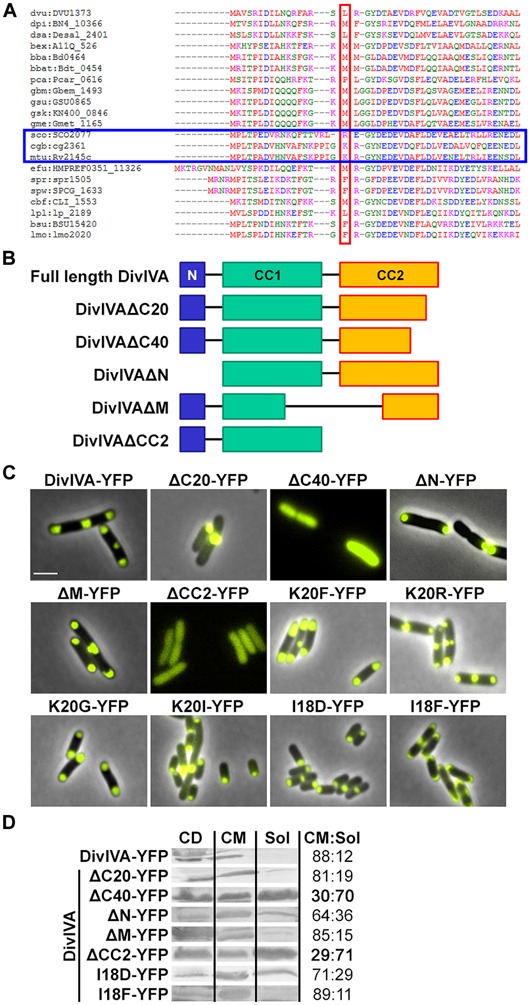
(A) Sequence alignment of N-terminal domains of several DivIVA proteins. Marked in red are AA residues that correspond to the F17 residue located at the tip of intertwined loops, according to the Bacillus subtilis DivIVA crystal structure. Polar growing actinobacteria such as Streptomyces, Corynebacterium, and Mycobacteria have a positively charged residue at this position (marked with a blue box). In the case of C. glutamicum, the corresponding AA is the lysine K20. Dvu: Desulfovibrio vulgaris, Dpi: Desulfovibrio piezophilus, Dsa: Desulfovibrio salexigens, Bex: Bdellovibrio exovorus, Bba: Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus, Bbat: Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus Tiberius, Pca: Pelobacter carbinolicus, Gbm: Geobacter bemidjiensis, Gsu: G. sulfurreducens PCA, Gsk: G. sulfurreducens KN400, Gme: G. metallireducens, Sco: Streptomyces coelicolor, Cgb: Corynebacterium glutamicum, Mtu: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Efu: Enterococcus faecium DO, Spr: Streptococcus pneumoniae R6, Spw: S. pneumoniae CGSP14, Cbf: Clostridium botulinum F, Lpl: Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1, Bsu: B. subtilis, Lmo: Listeria monocytogenes. Sequences were obtained from KEGG database. (B) Topology models of full length DivIVA and several truncation mutants that were generated and used in this study. DivIVAΔC20 and DivIVAΔC40 lack 20 or 40 AAs of their C-terminal ends. DivIVAΔN lacks the N-terminal domain, DivIVAΔM lacks a middle part of 154 AAs (144-298) and DivIVACC2 lacks the second coiled coil domain. (C) Fluorescence microscopy images of DivIVA variants that were heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli. Full length DivIVA-YFP localizes to both cell poles and the septum. DivIVAΔC20-YFP lost its proper localization character and forms huge, presumably non-functional, aggregates at mostly one cell pole. DivIVAΔC40-YFP as well as DivIVACC2-YFP localize in the cytoplasm, likely due to misfolding or lack of oligomerization. DivIVAΔN-YFP localizes to the poles; however, not always to both cell poles. DivIVAΔM-YFP localizes similar to wild type DivIVA. The DivIVA point mutants K20F and K20R localize similar compared to wild type protein. Mutants K20G-YFP and K20I-YFP showed polar localization, partly to one pole, comparable to DivIVAΔN-YFP. Mutant I18D-YFP showed no alterations in localization and membrane binding, whereas mutant I18F-YFP gives rise to increased membrane association. I18 is likely involved in membrane binding due to its hydrophobic character. (D) Ratios of non-aggregated, membrane attached vs. soluble DivIVA mutants. Full length DivIVA-YFP is 88% membrane attached and similar values were obtained from DivIVAΔC20-YFP and DivIVAΔM-YFP. DivIVAΔN-YFP is 64% membrane attached, implicating defects in membrane attachment that were drastically reduced for DivIVAΔC40-YFP and DivIVACC2-YFP to 30% and 29%, respectively. Mutant I18D-YFP had a minor decrease in membrane binding (71%) whereas I18F-YFP had a similar membrane affinity compared to WT DivIVA-YFP (89%). CD, cell debris fraction; CM, cell membrane fraction; Sol, soluble fraction. All numbers are mean values of at least three independent experiments.
