FIG 5.
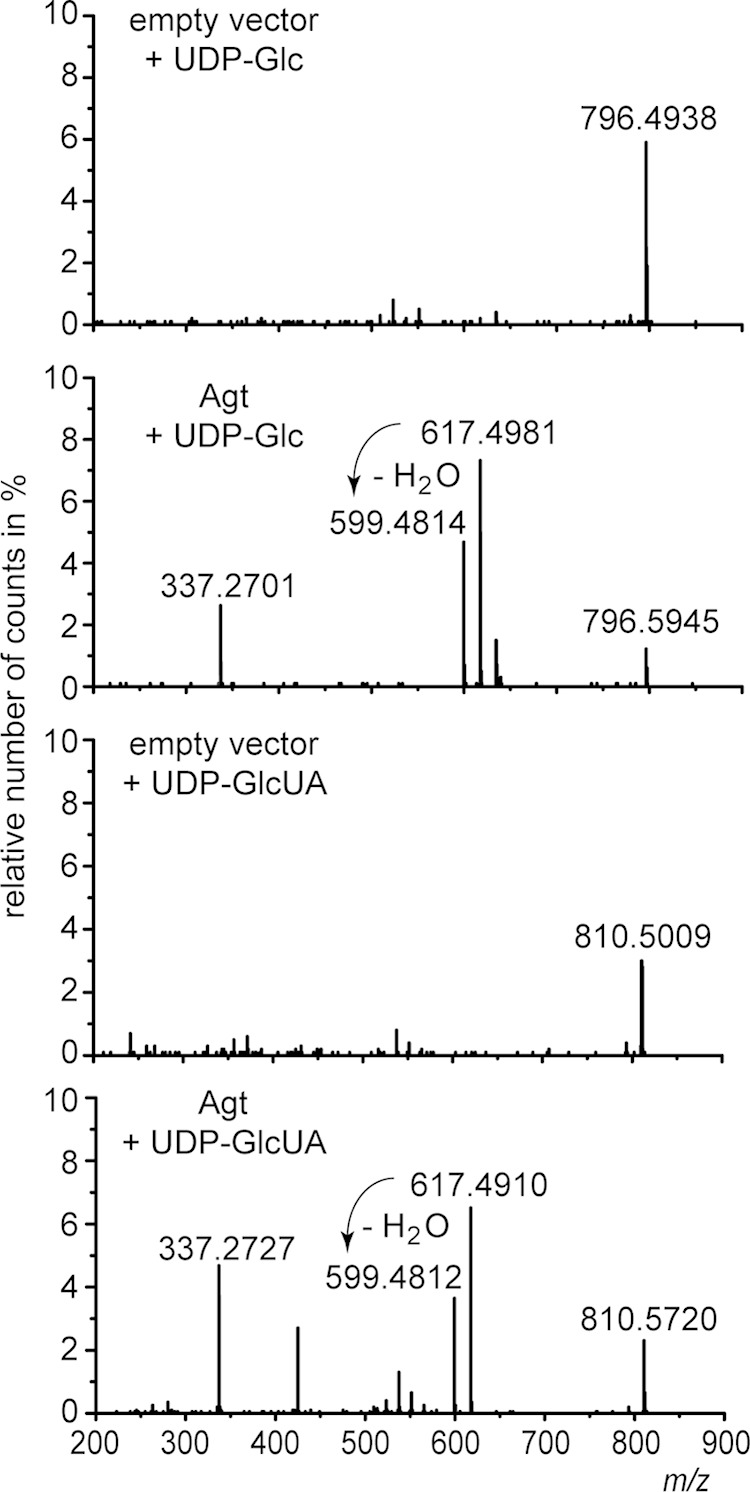
Q-TOF MS/MS spectra of MGlcD and GlcAD synthesized in enzyme assays with protein extracts from E. coli cells expressing Agt from Mesorhizobium or harboring the empty vector as a control. The assays were supplemented with DAG(18:2/18:2) as a sugar acceptor and UDP-glucose (UDP-Glc) or UDP-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcUA) as sugar donors. Parental ions with m/z 796.5934 or 810.5727 representing ammonium adducts of MGlcD or GlcAD, respectively, were selected in the positive-ion mode. The fragment ions with m/z 617.4981 (or 617.4910) represent the protonated form DAG(18:2/18:2), while fragment ions with m/z 599.4812 (or 599.4814) represent the protonated form of DAG(18:2/18:2) after loss of H2O; fragment ions with m/z 337.2701 (or 337.2727) represent the protonated form of MAG(18:2) after loss of H2O. The respective fragments were absent in the spectra of the control assays. The neutral losses of 197.1131 u (796.5945 u minus 599.4814 u) or 211.0908 u (810.572 u minus 599.4812 u) represent the ammonia adducts derived from glucose or glucuronic acid, respectively. These spectra prove the formation of both MGlcD and GlcAD (by supplementation of UDP-Glc or UDP-GlcUA, respectively) by Agt.
