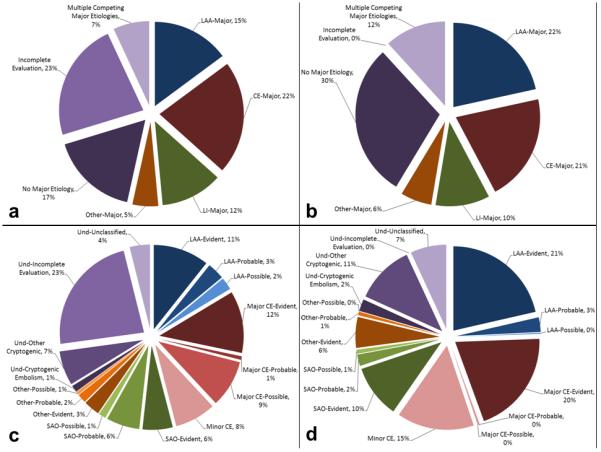
Figure 1.
Distribution of phenotypic and causative stroke subtypes: 1(a), phenotypic subtypes in the entire population; 1(b), phenotypic subtypes in the subset with complete vascular and cardiac investigation; 1(c), causative subtypes in the entire population; 1(d), causative subtypes in the subset with complete vascular and cardiac investigation. Please note that the term “incomplete evaluation” in Figures 1a and 1c designates an etiologic subgroup under “undetermined” category that is considered when diagnostic investigations are not performed in the absence of an identified etiology based on history and physical examination. According to this definition, a case with atrial fibrillation in history is not classified as incomplete evaluation when vascular and cardiac investigations are not done. The term “complete investigation” in Figures 1b and 1d, on the other hand, is solely based on availability of diagnostic tests indicating that brain imaging, vascular imaging, and cardiac evaluation are available. Hence, only 3,947 cases were classified as “incomplete evaluation”, while diagnostic investigations were not complete in 9,206 cases. Und: undetermined