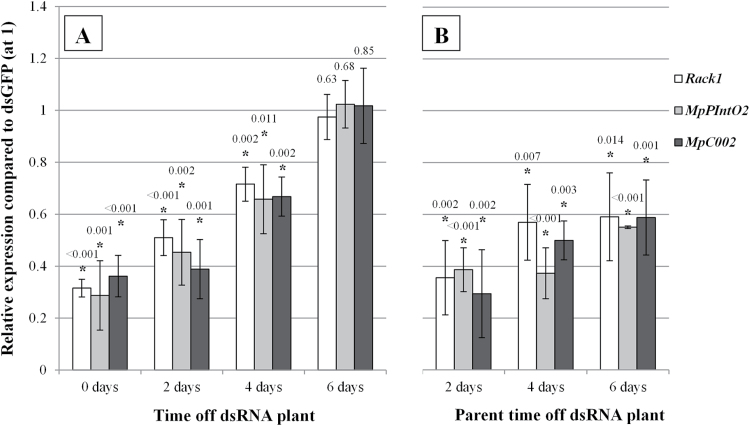
Fig. 2.
Continuous exposure to dsRNAs is required to attain maximal levels of down-regulation of aphid genes targeted by plant-mediated RNAi in adult aphids and progeny of these aphids. RNAi GPA were transferred to Col-0 plants then harvested at 0, 2, 4, and 6 d to test for target gene down-regulation by qRT-PCR. Second-generation nymphs were born from RNAi-exposed first-generation adults within 0–2 d of transfer to Col-0 plants. These nymphs were also collected at 2, 4, and 6 d. Relative expression of Rack1, MpPIntO2, or MpC002 was determined in adults (A) fed on dsRNA(target) and their nymphs (B) compared with dsGFP-fed equivalents. Bars represent average expression of the corresponding target gene at each time point for aphids reared on dsRack1 (white), dsMpPIntO2 (grey), or dsMpC002 (black) compared with aphids reared on dsGFP. Data represent mean expression levels ±SD for each target gene at each time point for three biological replicates. Relative target gene expression values were normalized to the expression level of dsGFP aphids set at 1. An asterisk indicates a significant difference compared with the dsGFP control (Student’s t-test, n=3, P<0.05), and P-values (to three decimal places) corresponding to individual data points are displayed above each bar.