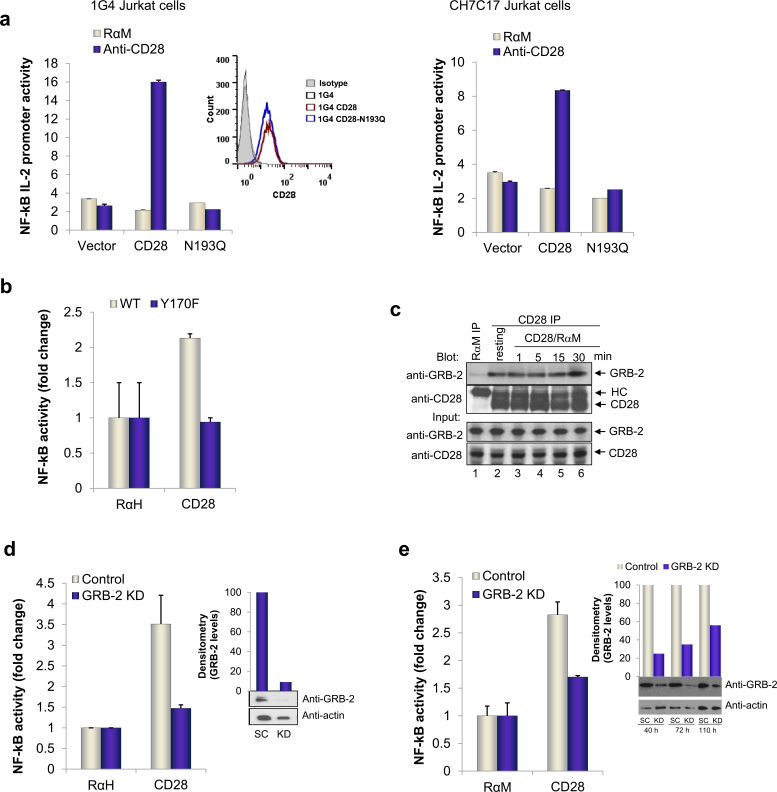
Fig. 2.
GRB-2 connects proximal signals to regulate CD28 driven NF-κB pathway. (a) Cd28−/− cells were reconstituted with empty vector, WT CD28 or N193Q mutant. FACS histogram shows surface expression of WT or N193Q CD28 by staining with FITC labeled antibodies to CD28. Right panel shows another representative experiment obtained from CH7C17, CD28 deficient cell line. NF-κB luciferase activity was measured after stimulation with indicated antibodies. (b) Y170F knock-in mutant primary T-cells were used in conjunction with wild type primary cells. Luciferase firefly units were normalized to background Renilla values. (c) Binding of Grb-2 to CD28. Jurkat T-cells, either left unstimulated (lane 2) or stimulated with anti-CD28/rabbit anti-mouse IgG for 1, 5, 15 and 30 min (lanes 3–6) were lysed, immunoprecipitated with anti-CD28 and blotted for Grb-2. Immunoprecipitation with rabbit anti-mouse IgG served as a negative control (lane 1). Input panels: blotting of cell lysates with Grb-2 (upper panel) or CD28 (lower panel) served as a loading control. siRNA knock-down of GRB-2 in primary cells (d) and Jurkat cells (e) and its effects on NF-κB pathway after 48 and 72 h of knock-down respectively. Efficiency of knock-down was assessed by western blotting as shown in insets (SC: scrambled and KD: knock-down) and quantified by normalizing to endogenous actin levels (inset column chart). All siRNA were purchased from Dharmacon (Thermo Scientific).