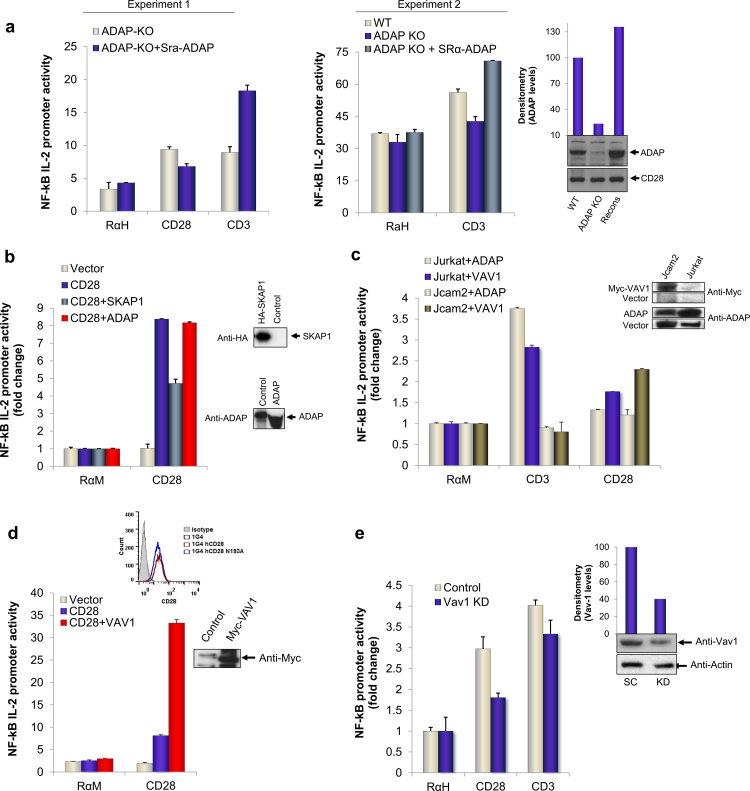
Fig. 3.
Normal CD28 but defective TCR mediated NF-κB pathway in ADAP KO primary and LAT deficient Jurkat cells. (a) CD3+ cells isolated from spleens of adap−/− (silver bars) or wild type (blue bars) mice were used for NF-κB IL-2 promoter assay by transfecting with reporter plasmids followed by stimulation with control, anti-CD28 or anti-CD3 antibodies. Right panel, NF-κB activity in adap−/− (blue bars) compared to controls wild type (silver bars) or adap−/− T-cells transfected with exogenous ADAP (green bars). Efficiency of transfection was assessed by western blotting and normalized to endogenous CD28 levels as shown by column chart (inset). Each point is average of triplicate with SD. (b) NF-κB activity measured in CD28 reconstituted Jurkat 1G4 cells transfected with adapters SKAP1 or ADAP (Fyb) or control plasmids as shown. NF-κB activity was measured as above. (c) NF-κB reporter activity in LAT deficient (Jcam2) cells, either transfected with VAV1 (green bars) or ADAP (silver bars) when engaged with control (RaM), anti-CD28 or anti-CD3 antibodies. Wild type (Jurkat) transfected with respective plasmids were used as control. All values are relative luciferase units and average of triplicates with standard deviations. (d) Reconstitution of Cd28−/− Jurkat cells with VAV1 or respective controls. NF-κB activation in response to CD28 was measured as above. (e) siRNA knock-down of VAV1 in primary T-cells for 48 h. NF-κB activity was measured from reporter plasmids when cells were stimulated for 6 h with control (RαH), anti-CD28 or anti-CD3 antibodies. Knock-down efficiency was detected by western blotting of endogenous proteins and quantified by densitometric analysis and shown as actin normalized values in column chart (inset). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)