Figure 1.
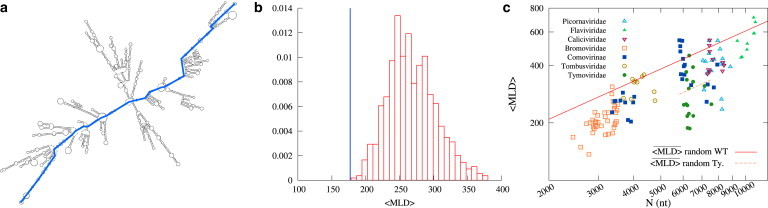
(a) Example of a typical fold of the entire brome mosaic virus (BMV) RNA2 sequence. The maximum ladder distance (MLD) of the folded sequence is highlighted. (b) Thermally averaged MLD, 〈MLD〉, of the WT BMV RNA2 sequence (blue line) and the distribution of 〈MLD〉 values obtained for random RNA sequences of same length and composition as the WT sequence. (c) 〈MLD〉 value of viral ssRNA sequences versus the sequence length N (in nucleotides). Different virus families are represented by different colors and symbols. (Red solid line) Power law of Eq. 3 for the expected values of 〈MLD〉 for random RNA sequences, constrained only by their overall viral-like nucleotide composition. Due to their atypical nucleotide composition, Tymoviridae are not represented by Eq. 3, and the corresponding scaling law for Tymoviridae-like random RNA sequences, , is shown (orange dashed line). See the Supporting Material for further information. (To see this figure in color, go online.)
