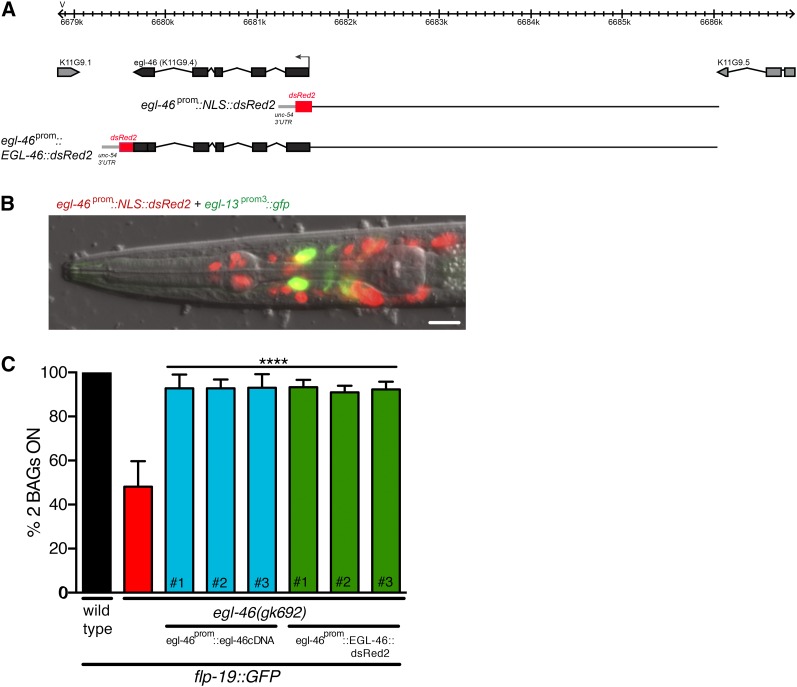
Figure 2.
egl-46 rescue of BAG neuronal fate defects. (A) Schematic representation of the egl-46 genomic locus. The ATG codon is marked with an arrow and the exons are represented as black blocks. The egl-46 translational reporter was constructed by driving egl-46 genomic DNA with dsRed2 coding sequence under the control of the 4.5-kb egl-46 promoter. The transcriptional reporter was constructed using the 4.5-kb promoter to drive nuclear-localized dsRed2 (NLS::dsRed2). (B) The 4.5-kb egl-46 promoter drives NLS::dsRed2 expression in multiple nuclei in the head. Colocalization (yellow) of NLS::dsRed2 was observed with cytoplasmic gfp driven by an egl-13 promoter in the BAG neurons. Note that we only rarely observed colocalization with the BAG marker, suggesting that the egl-46 promoter drives expression in the BAG neurons in a transient manner. Ventral view, anterior is to the left. Bar, 20 μm. (C) Transgenic expression of the egl-46 cDNA or egl-46 genomic sequence fused to dsRed2 under the control of the egl-46 promoter rescues the egl-46(gk692) mutant loss of flp-19prom::gfp expression. n > 50. ****P < 0.0001. # refers to independent transgenic lines.