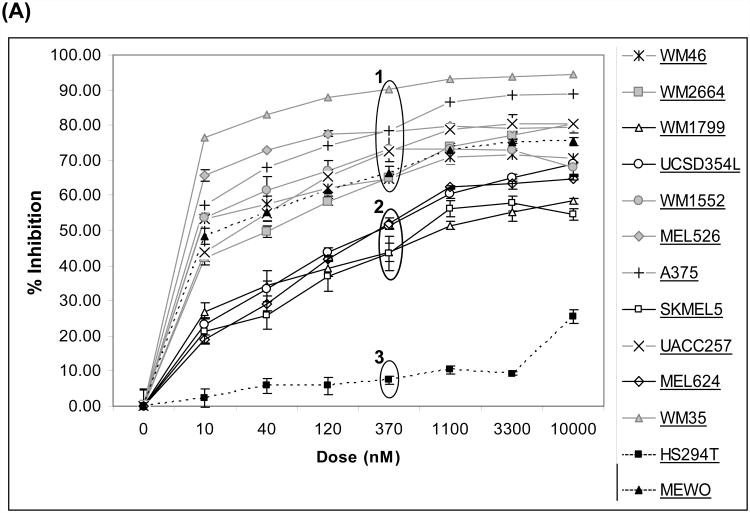
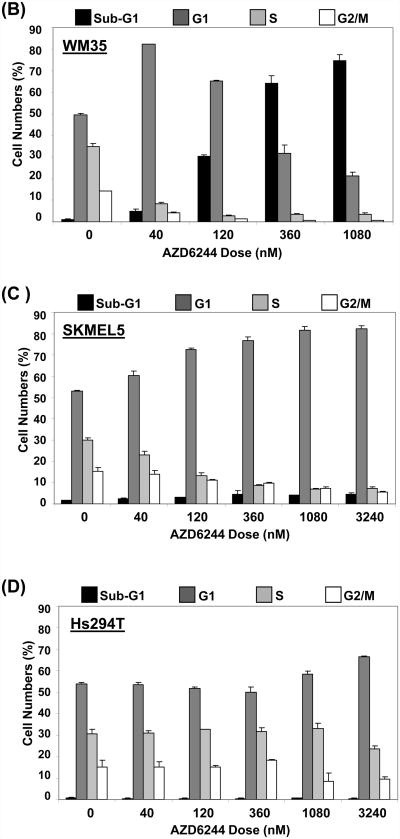
Figure 1. Growth and survival inhibition by AZD6244.
(A) Growth inhibition in human melanoma cell lines treated with AZD6244 for 48 h. X-axis, concentration of AZD6244 (nM); Y-axis, % growth inhibition. Groups of cells with high (“1”), moderate (“2”), and low (“3”) sensitivity are indicated. Cells with data points connected by dotted lines are wild-type for Braf, all other cell lines have Braf mutations. Data points are the average of 3 replicates; error bars, standard deviation. (B) Cell cycle analysis of WM35 cells (Group 1) after 72 h treatment AZD6244. X-axis, concentration of AZD6244 (nM); Y-axis, % of cell population. The Sub-G1 (dead cells), G1, S, and G2/M phases of the cell cycle are indicated by black, dark grey, light grey and white bars respectively. Each bar is the average of two replicates; error bars, standard deviation. (C) Cell cycle analysis of SKMEL5 cells (Group 2). (D) Cell cycle analysis of HS294T cells (Group 3).