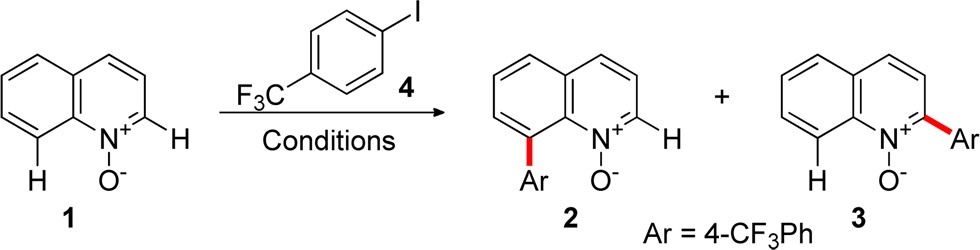
Table 1. Reaction Development for the Palladium-Catalyzed C8 Arylation of Quinoline N-Oxidesa.
| yield
(%) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | catalyst (5 mol %) | AgX (amt (equiv)) | additive (amt (equiv)) | 1 | 2 (C8) | 3 (C2) | C8/C2 (2/3) |
| 1 | Pd(OAc)2 | AcOH (10) | 91 | 8 | 0.6 | 12:1 | |
| 2 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc (3) | AcOH (10) | 38 | 39 | 3 | 13:1 |
| 3 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc (3) | DMF (10) | 29 | 5 | 36 | 1:7 |
| 4 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc (3) | tBuOH (10) | 50 | 7 | 41 | 1:6 |
| 5 | PdCl2 | AgOAc (3) | AcOH (10) | 7 | 17 | 2 | 9:1 |
| 6 | Pd(TFA)2 | AgOAc (3) | AcOH (10) | 27 | 40 | 11 | 4:1 |
| 7 | Pd(OAc)2 | Ag2CO3 (0.5) | AcOH (10) | 29 | 23 | 3 | 8:1 |
| 8 | Pd(OAc)2 | Ag3PO4 (0.5) | AcOH (10) | <2 | 73 | <2 | >30:1 |
| 9 | Pd(OAc)2 | Ag3PO4 (0.5) | AcOH (30) | 8 | 78 | <2 | >30:1 |
| 10 | Pd(OAc)2 | Ag3PO4(0.5) | AcOH (30)/H2O (5.5) | 1 | 95 | 4 | 23:1 |
| 11b | Pd(OAc)2 | Ag3PO4(0.5) | AcOH (30)/H2O (5.5) | 6 | 90 | 3 | 30:1 |
| 12c | Pd(OAc)2 | Ag3PO4(0.5) | AcOH (30)/H2O (40) | 28 | 65 | <2 | >30:1 |
Yields were determined by 1H NMR analysis with 1,4-dimethoxybenzene as an internal standard added prior to workup. Reaction conditions: 1 (0.2 mmol), 4 (3 equiv), with the catalyst and the additives under Ar for 12 h at 120 °C.
Reaction was run under microwave irradiation at 180 °C for 45 min.
Reaction was run under microwave irradiation at 180 °C for 10 min.
