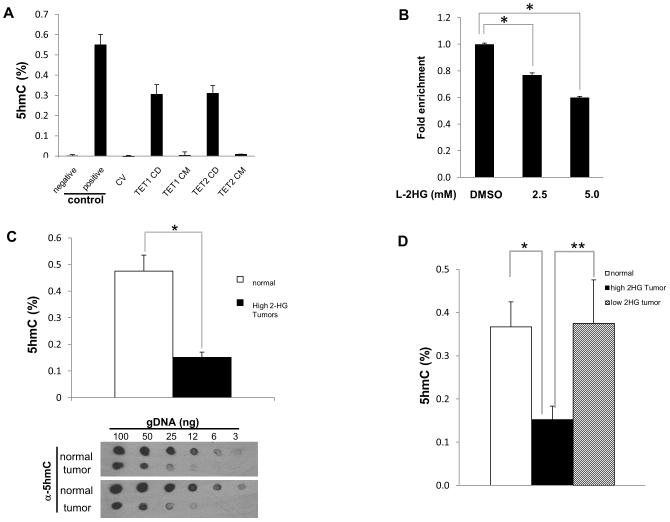
Figure 2. Increased L-2HG is associated with loss of 5-hmC in RCC tumors.
(A) Validation of ELISA for 5hmC. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids expressing control vector (CV), TET1 wild-type catalytic domain (CD) and mutant catalytic domain (CM), TET2 wild-type catalytic domain (CD) and mutant catalytic domain (CM). Cells were harvested and genomic DNA was examined to determine 5hmC level. (B) HK-2 renal epithelial cells were treated with L-2HG octyl ester for 4 hours and assayed for 5hmC levels via ELISA. (C) 5hmC levels between normal and high L-2HG RCC tumor samples were analyzed by ELISA (upper panel) and dot blot assay (lower panel). (D) 5hmC levels in normal, low 2HG tumors, and high 2HG tumors were determined by ELISA. Error bars represent standard error of mean. (*) p <0.005, (**) p <0.05.