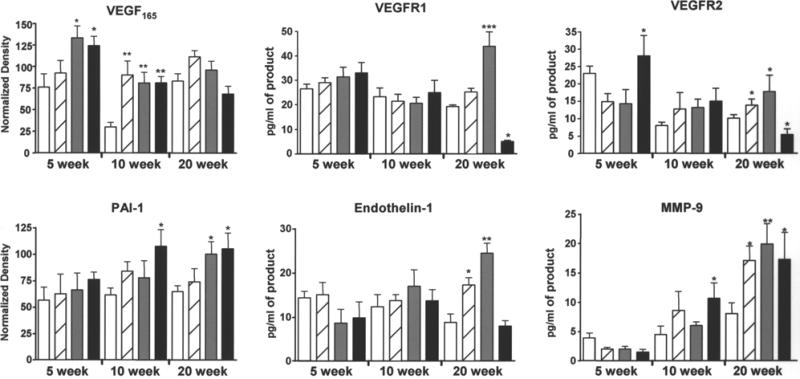
Fig. 5.
Chronic AsIII exposure differentially affected cardiac angiogenic and remodeling gene expression. At the termination of exposure, hearts were collected from the mice in Fig. 3. Apical and atrial sections were snap frozen and RNA was isolated and analyzed as describe in Materials and Methods. Conventional (vascular endothelial cell growth factor [VEGF165] and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 [PAI-1]) or real-time RT-PCR was used to measure specific mRNA levels relative to 18S RNA. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of corrected mRNA levels from five mice. Treatments were as follows: no added AsIII (open bar), 50 ppb AsIII (striped bar), 250 ppb AsIII (gray bar), and 500 ppb AsIII (black bar). The data were analyzed for differences by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test for significance. Significant difference from time-matched control is designated by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase-9.