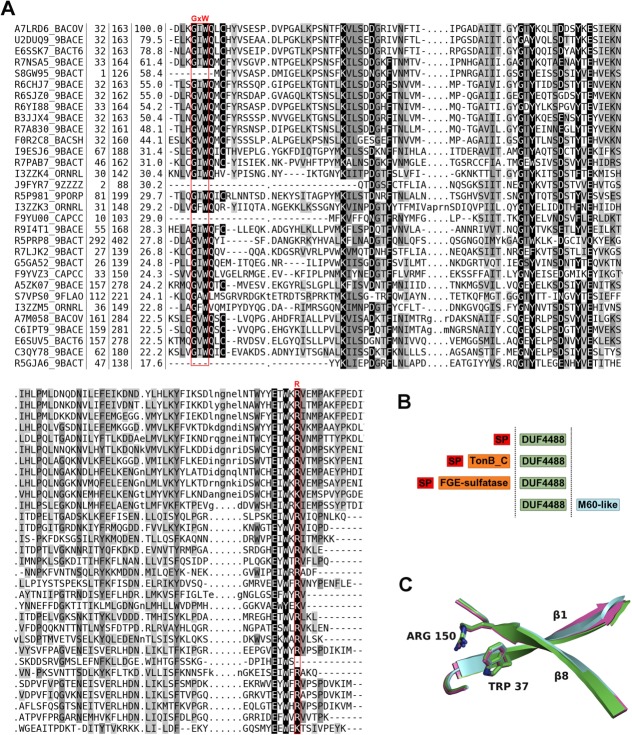
Figure 5.
Sequence alignment, family architecture and calycin signature residues in the DUF4488/PF14869 Pfam family. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of DUF4488/PF14869 Pfam family members using a redundancy cutoff of 80% sequence identity. For each sequence, we report the UniProtKB id, the position of first and last residue in the alignment, the percent sequence identity with respect to A7LRD6_BACOV (i.e., BACOVA_00364) and the amino acid sequence. Shades of gray in alignment columns reflect average similarity at a given position as calculated from the BLOSUM62 amino acid substitution matrix (black most conserved, white least conserved). Dashes (-) represent deletions. Lower case letters represent inserted residues and dots (.) in the same columns are fillers for sequences lacking the inserted residues. The red boxes mark the position of residues involved in the calcyin motif (GxW/R). Alignment visualized with Belvu (http://sonnhammer.sbc.su.se/Belvu.html). (B) General architecture of DUF4488/PF14869 family members. Out of 146 members, 125 contain a single DUF4488 domain; 19 also contain a TonB_C domain, one contains a M60-like domain, and one a FGE-sulfatase domain. ‘SP’ indicates a predicted signal peptide (according to PHOBIUS19). (C) Superposition of strand 1 and strand 8 of the β-barrel of 4gzv (green), 4iab (cyan), and 4i95 (magenta) in cartoon representation, highlighting the calycin motif residues tryptophan and arginine packing against each other.